Category: Teaching
What You Might Have Missed in April–What’s up in May
Here are the most-read posts for the month of April
- National Library Week April 3-9
- Preparing for College or Career
- Long-Term Benefits of Bilingual Education
- How to Become a Tech Teacher
- Tech Tools for Reading Fluency
- Assistive Technology in Colleges
- Resources to Teach Taxes
- How to Make a Program Easy to Find
- 18 Easter Websites and Apps
- Earth Day Classroom Activities
Here’s a preview of what’s coming up in May:
- Kiddom’s New Lesson Launch
- Websites on Architecture and Engineering
- End of School Year Tasks
- 5 Tips to Involve Parents
- Does MS Word Have ‘Research’?
- Memorial Day Websites and Projects
- Must-have Apps for Curious Students
- Digital Reading for Summer

Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
Tech Teacher Appreciation Week
I posted this article last year, got lots of reads, so am republishing with some updates. I’ve included information about:
- How tech teachers are different than other teachers
- Why tech and the teacher who manages it in your school has become more important than ever
- How to talk to a tech teacher (hint: they’re a little different; heed these suggestions)
- Gifts tech teachers will love
Tech Teacher Appreciation Week: The First Full Week of May
 There’s always been something mystically cerebral about people in technical professions like engineering, science, and mathematics. They talk animatedly about plate tectonics, debate the structure of atoms, even smile at the mention of calculus. The teaching profession has our own version of these nerdy individuals, called technology teachers. In your district, you may refer to them as IT specialists, Coordinators for Instructional Technology, Technology Facilitators, Curriculum Specialists, or something else that infers big brains, quick minds, and the ability to talk to digital devices. School lore probably says they can drop a pin through a straw without touching the sides.
There’s always been something mystically cerebral about people in technical professions like engineering, science, and mathematics. They talk animatedly about plate tectonics, debate the structure of atoms, even smile at the mention of calculus. The teaching profession has our own version of these nerdy individuals, called technology teachers. In your district, you may refer to them as IT specialists, Coordinators for Instructional Technology, Technology Facilitators, Curriculum Specialists, or something else that infers big brains, quick minds, and the ability to talk to digital devices. School lore probably says they can drop a pin through a straw without touching the sides.
When I started teaching K-8 technology, people like me were stuffed into a corner of the building where all other teachers could avoid us unless they had a computer emergency, pretending that what we did was for “some other educator in an alternate dimension”. Simply talking to us often made a colleague feel like a rock, only dumber. When my fellow teachers did seek me out — always to ask for help and rarely to request training — they’d come to my room, laptop in hand, and follow the noise of my fingers flying across the keyboard. It always amazed them I could make eye contact and say “Hi!” without stopping or slowing my typing.
That reticence to ask for help or request training changed about a decade ago when technology swept across the academic landscape like a firestorm:
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
How to Become a Tech Teacher
I know from personal experience that tech teachers are in short supply. It’s not unusual for a school to transfer the PE teacher or 2nd grade teacher into the Tech Teacher job because they can’t find anyone else for that position. ZDNet has a great article addressing the subject:
How to get into tech as a teacher
Tech careers are in high demand. The tech field attracts many career-changing professionals with strong salaries and diverse career paths. And teachers are uniquely positioned to move into tech.
If you’ve wondered how to get into tech as a teacher, you may think the field is intimidating. But while some tech careers require coding skills, many do not. By highlighting your transferable skills and educational strengths, you can move into careers like instructional designer, eLearning developer, training specialist, or technical writer.
More about teaching tech
- Teacher Appreciation Week–Gifts for the Tech Teacher (humorous)
- What’s a Tech Teacher Do With Their Summer Off?
- A Day in the Life of a Tech Teacher (humorous)

Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
What You Might Have Missed in March–What’s up in April
Here are the most-read posts for the month of March
- Social Media or COVID: Which is more dangerous to students?
- 5 (free) Posters about Learning
- Websites that add sparkle (and learning) to Spring
- Guiding Students through the Crisis in Ukraine
- A Lesson Plan for Addressing What’s in the News
- Invention Convention is coming
- Celebrate Pi Day and Maths Day
- Using VR to Visualize Complex Information
- 23 Websites on Biomes, Habitats, Landforms
- 7+ Websites to Teach Financial Literacy
Here’s a preview of what’s coming up in April:
- Preparing for College or Career
- How to Become a Tech Teacher
- Tech Tools for Reading Fluency
- Resources to Teach Taxes
- Easter Websites
- Earth Day Activities
- Digital Literacy
- Create a Macro
- Websites on Architecture/Engineering

Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
Has Teaching Changed since the Pandemic?
Ask a Tech Teacher contributor, Christian Miraglia, wrote an interesting article on changes in teaching since the pandemic. I think you’ll find a lot to relate to:
Has Teaching Changed Since the Pandemic?
March 13, 2019, for many educators in California and nationwide, was a day that will forever be etched in their memories. It was the day that many school districts closed temporarily, or so they thought, due to the spread and uncertainty of COVID-19. What nobody could have seen was that these closures would become more permanent and reshape the educational landscape for years to come. Changes to daily instruction have become the norm as students were absent due to illness, teachers were absent due to COVID-19 exposure or their children having been infected or exposed, in-face instruction shifting to online and then back to face-to-face.
Recently I listened to K-12 educators at a session hosted by a local university designed to have teachers meet and share their experiences from the past two years. The output of emotions from these brave educators who detailed what it is like to teach during this challenging time was gut-wrenching.
The resiliency of these educators is to be commended as they navigated the daily challenges of policy changes, students coming and leaving, the caring for themselves and their children. In listening to them, a common theme resonated from the group, the value of networking.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
What You Might Have Missed in February What’s up in March
Here are the most-read posts for the month of February:
- Groundhog Day and the 100th Day of School
- #WorldReadAloudDay February 2
- Simulations as a Teaching Strategy
- Model Teaching–How Today’s Educators Learn
- Translate Webpages In a Second
- 14 Valentine Sites For Students
- How Does the Metaverse Fit into Education?
- Random Acts of Kindness Day
- Track Your Stuff
- Logitech Pen–No Setup, No Batteries, No Problems
Here’s a preview of what’s coming up in March:
- Subscriber Special
- Social Media or COVID: Which is more dangerous to students?
- Free Posters
- Invention Convention
- Pi Day
- Apps for Curious Students
- St. Patrick’s Day REsources
- Resources for Architecture/Engineering
- World Backup Day
- How Twitter makes you a better writer

Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
Model Teaching–How Today’s Educators Learn
Thousands of teachers every year take education classes to renew their license, move up to the next salary range at their school (I did that–often), or learn teaching skills they didn’t get in their degree program (like remote teaching or in-depth technology). This used to mean enrolling at your local college or online institution. Now, the right classes may not be available, or available but at the wrong time, or the class is full before you get a chance to enroll. You may find a program that meets some of your requirements but not all and wonder if you should settle. What you need–and want–is one program that fulfills your needs, not what they think you need.
I recently received an email from the folks at Model Teaching. They have a huge catalog of K-12 education training classes that are offered online, on open schedules, and at affordable rates. Enrollment includes all required materials–no extra charges for books or subscriptions–as well as templates that can be immediately applied to your teaching.
I realized this program was what lots of my colleagues were looking for but couldn’t find. Until now.
What is Model Teaching?
Model Teaching is an online educator training program with a goal not only to provide teaching knowledge but to improve overall student performance. Classes are designed to help new and experienced K-12 teachers master concepts and immediately apply them to their lessons. The catalog include topics relevant to today’s K-12 education offered in a variety of approaches that meet teacher needs. Some are a short introduction to a concept (what they call Quick Classes–usually about an hour). Others, offer a certificate (multi-week deep dive into a topic) or grad school credit with official transcripts through one of their partner Universities (such as University of Massachusetts and the University of the Pacific).
All classes follow an easy-to-use course design:
- establish goals–what students will learn by the end of the class
- provide a clear module-based learning path culminating in a ready to use action plan
- include resources for both teachers and students in a variety of modalities–text, video, and downloadable resources
- assess success at completion
How to get started
Model Teaching makes it easy to get started:
- Set up an account–quick and easy; nothing tricky
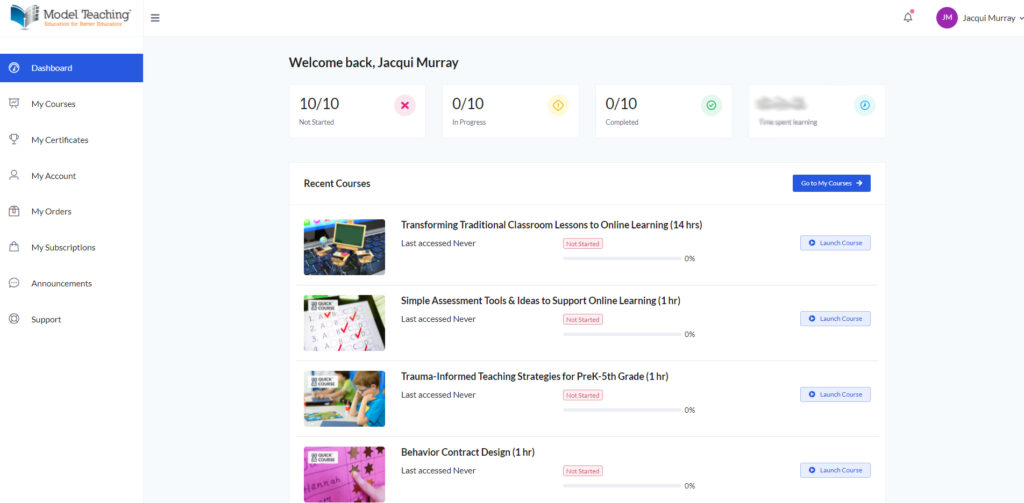
- All accounts include a dashboard to track courses taken/being taken, certificates earned, modules completed in each class, which classes in your overall plan are completed, how long you’ve spent working on the class, and more. Here’s my dashboard:
As you proceed through your personal program, check this often to track progress.
- Search the course catalogue by 1) credit type (Quick Classes, PD, or grad school credit), 2) content, 3) Academic partner (the college or University you are sending credits to), or 4) grade level. Topics include but not limited to:
- Flipped Classrooms
- Student-led Classroom Management
- Elementary Math
- Writing Prompts
- Blended Learning
- Transforming Traditional Classroom Lessons to Online Learning
- Academic Intervention for Students with Disabilities and Special Needs
- UDL
- Bloom’s Taxonomy
- Effective Writing Prompts for All Students
- Click the class you’re interested in for more detail. Here are two examples. The top one is a professional development class, the bottom one for grad school credits:
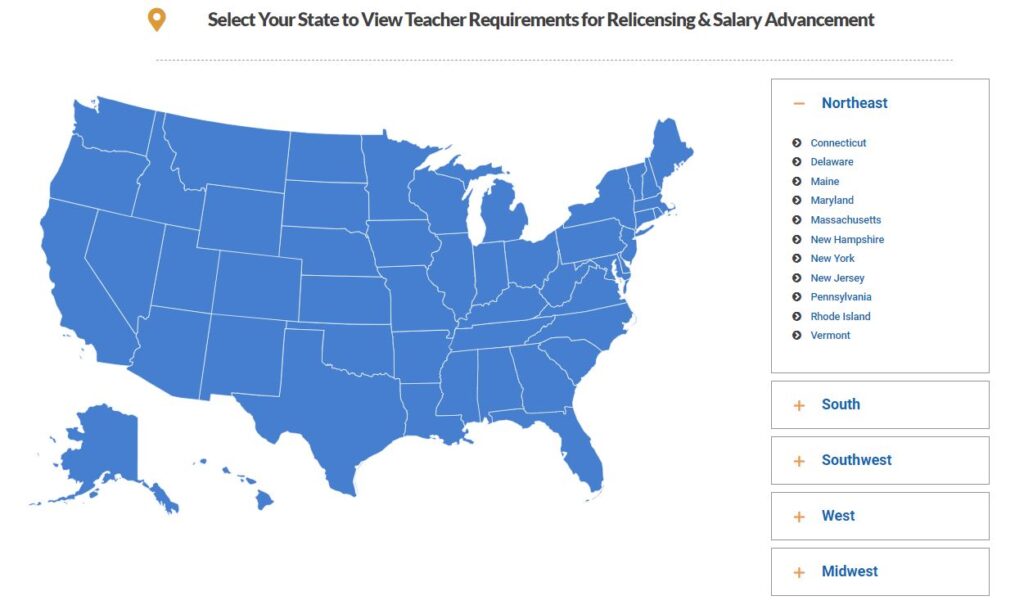
- If you aren’t sure what classes to take, Model Teaching provides an interactive map. Select your state and then read about the requirements:
- Once you start a class, proceed at your own pace, as fast or slow as works for you. You can watch the video, rewatch, submit assignments and assessments when you’re ready. Your dashboard tells you how much time you’ve spent and how much remains before you must complete the course.
- At completion, students receive a certificate (or grad school credit) and feedback from certified instructors.
What I really like about Model Teaching
 There are many pieces to this learning platform that are unique in the education industry. I can’t list them all, but here are a few I particularly liked:
There are many pieces to this learning platform that are unique in the education industry. I can’t list them all, but here are a few I particularly liked:
- Though online, classes require only basic tech knowledge. Participation is compatible with all platforms (Mac, PC, Chromebooks, smart phones, tablets) and all browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Edge, and others). A PDF program (like Adobe Reader) and Microsoft Word or Google Docs will satisfy most (all?) course requirements.
- I can sign up for one class or build my own PD bundle at a discounted price.
- At any time, I can view my gradebook to see how I’m progressing. I never wonder if I’m passing.
- Learning is presented in a variety of modalities, such as text and audio. I can also download the video as a PDF.
- Courses follow a standardized format so I always know what to expect.
- Classes include lesson templates that I can immediately apply to my classes, during or after the class is taken.
- Courses start as low as $10 and there are discounts for multiple courses and for schools/districts. There is also a free trial, to be sure this approach fits my way of learning.
- If you are an administrator signed up for a school subscription, you can assign classes to teachers based on individual needs, build learning plans for a team, assign a subscription of all courses to every teacher on campus and let them pick courses for their professional development (PD). Administrators can monitor progress of everyone enrolled in courses, and more from their dashboards.
Still curious? Check out this three-minute overview of Model Teaching:
Professional Development Courses – Model Teaching from Adam Pond on Vimeo.
Easy to get started, flexible plans, relevant teaching topics–Model Teaching is an excellent choice for great teachers.
–Note: Model Teaching partnered with Ask a Tech Teacher for this overview, but opinions are my own.
–For more information, visit their website or their Facebook page
Jacqui Murray has been teaching K-18 technology for 30 years. She is the editor/author of over a hundred tech ed resources including a K-12 technology curriculum, K-8 keyboard curriculum, K-8 Digital Citizenship curriculum. She is an adjunct professor in tech ed, Master Teacher, webmaster for four blogs, an Amazon Vine Voice, CSTA presentation reviewer, freelance journalist on tech ed topics, and author of the tech thrillers, To Hunt a Sub and Twenty-four Days. You can find her resources at Structured Learning.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
What You Might Have Missed in January–What’s up in February
Here are the most-read posts for the month of January
- Public Domain Day and Happy New Year!
- How to Change the Dynamics of Peer-to-peer Learning with Tract
- Top 10 Hits and Misses for 2021
- Ready To Go Back To School? 7 Fun Lesson Ideas To Start The New Year
- 4 (free) Posters About Reading
- Practices of Tech-savvy Teachers
- 23+ Websites on Animals
- 5 YouTube Features for Teachers
- Google Earth Lesson Plans
- How Minecraft Teaches Reading, Writing and Problem Solving
Here’s a preview of what’s coming up in February:
- Groundhog Day
- World Read Aloud Day
- Simulations as a Teaching Strategy
- Grading Practices
- 3D Printing Websites
- Tech Tips
- Valentine’s Day Online Resources
- Free Posters
- The Metaverse and Education
- President’s Day Activities
- Teacher Training: Model Teaching
- Random Acts of Kindness Day
- Instagram: A Student Vehicle for Social Change

Jacqui Murray has been teaching K-18 technology for 30 years. She is the editor/author of over a hundred tech ed resources including a K-12 technology curriculum, K-8 keyboard curriculum, K-8 Digital Citizenship curriculum. She is an adjunct professor in tech ed, Master Teacher, webmaster for four blogs, an Amazon Vine Voice, CSTA presentation reviewer, freelance journalist on tech ed topics, and author of the tech thrillers, To Hunt a Sub and Twenty-four Days. You can find her resources at Structured Learning.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
Practices of Tech-savvy Teachers
Are you struggling with all the tech required for remote and hybrid teaching? Education Week shares what tech-savvy educators are using to make this work:
5 Practices of Truly Tech-Savvy Teachers
 Education Week caught up with select teachers and instructional coaches who shared their thoughts on some essential practices to effectively implement technology into the practice of teaching. Some were discovered or honed during the pandemic. All offer lessons for job seekers wanting to present in-demand knowledge and skills, as well as districts and schools that are seeking truly tech-savvy teachers.
Education Week caught up with select teachers and instructional coaches who shared their thoughts on some essential practices to effectively implement technology into the practice of teaching. Some were discovered or honed during the pandemic. All offer lessons for job seekers wanting to present in-demand knowledge and skills, as well as districts and schools that are seeking truly tech-savvy teachers.
Ask a Tech Teacher has reviewed a list of easy-to-use, intuitive tech tools we think will make your teaching job easier. Check otu these articles:
How to Evaluate Programs You’ve Never Used in Less Than Seven Minutes
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
New Teachers–From Pandemic to the Classroom
 This is a great article for new teachers who might not have seen the traditional classroom experience. One teacher offers tips to help new starters who did their training in lockdown to feel at home in their classroom:
This is a great article for new teachers who might not have seen the traditional classroom experience. One teacher offers tips to help new starters who did their training in lockdown to feel at home in their classroom:
New Teachers: 10 Ways to Claim Your Classroom Space
The first terms as an early career teacher are daunting: and it can be a while until you feel completely settled in your new role. But your classroom is the place you’ll spend the majority of your time, and it’s crucial that you feel ownership of it, as well as at home within it.
Many of you will have carried out a lot of your teacher training remotely – and therefore, may feel a little uncertain about how to claim classrooms as your own. Here’s my advice.
Here’s more advice for new teachers from Ask a Tech Teacher:
6 Tech Best Practices for New Teachers
New Tech Teacher? I Understand You
Technology and Teaching: A Conversation with Teachers
13 Tips for New Tech Teachers You Don’t Want to Miss

Jacqui Murray has been teaching K-18 technology for 30 years. She is the editor/author of over a hundred tech ed resources including a K-12 technology curriculum, K-8 keyboard curriculum, K-8 Digital Citizenship curriculum. She is an adjunct professor in tech ed, Master Teacher, webmaster for four blogs, an Amazon Vine Voice, CSTA presentation reviewer, freelance journalist on tech ed topics, and author of the tech thrillers, To Hunt a Sub and Twenty-four Days. You can find her resources at Structured Learning.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More