Category: Webtools
Go Paperless for Earth Day
 Earth Day is April 22nd. Someone in your school, maybe the parent group, will raise the question of WHY NOT a paperless classroom? Everyone will nod their heads, agree this is a revolutionary idea, and move on when Earth Day passes.
Earth Day is April 22nd. Someone in your school, maybe the parent group, will raise the question of WHY NOT a paperless classroom? Everyone will nod their heads, agree this is a revolutionary idea, and move on when Earth Day passes.
Really, though: There are benefits to adopting web-based alternatives to paper:
- it’s easy to collaborate when everything’s online
- nothing gets soda dripped on it or eaten by the dog
- students can easily collaborate without requiring parent time and gas fumes
- teachers can answer questions in a timely manner
- teachers can provide feedback on projects that students respond to and resubmit
- student work is easy to copy, backup, and share as needed
To kickstart your paperless digital classroom requires a modicum of preparation. Take a few weekends this summer to set up a class blog and class website and get comfortable with the digital side of your school. This may include:
- Google Apps for Education and/or Google Classroom–this serves as a basic digital portfolio for students, a collaborative tool with classmates, the teacher’s inbox and her tool for returning graded and analyzed student work.
- an LMS like Edmodo, Otus, or MyBigCampus–these often include an interactive gradebook, parent inclusion devices, a student discussion forum, polls, a way to collect and share resources, a class calendar, and access across a variety of digital devices.
- digital portfolios for students–this can be accomplished with whatever LMS you use, Google Apps, Google Classroom, or even Dropbox
Three pieces that you especially want to look for:
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
4 Ways Students Can Plan Their Writing
Few people can sit down and start writing. Most of us hem and haw as we mentally walk through how to get from introduction to conclusion. It’s called ‘prewriting’ and students are no different. Where they diverge from you and I is they haven’t tested all the available methods for planning a story, constructing non-fiction, or building the evidence-based argument. It’s up to us–as their teachers–to introduce these alternatives so they can pick one best suited to their learning and communication style.
Disclaimer: These are presented in a random order because what works for your students will depend in large extent upon the writing method used in your school, whether its the 6+1 Traits, Common Core Writing Standards, or the tried-and-true who-what-when-where-why.
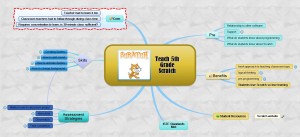 Brainstorm/Mindmap
Brainstorm/Mindmap
Brainstorming, also called ‘mindmapping’, is a collaborative visual approach to thinking through and presenting ideas. It enables students to come up with many ideas without worrying about whether it’s realistic. It’s great for collaborative writing, note-taking, or an individual effort.
Here are basics for brainstorming in the classroom:
- There are no wrong answers.
- Get as many ideas as possible.
- Don’t evaluate ideas–just record them.
- Build on the suggestions of others.
- Stress quantity over quality–get as many ideas as possible. Sort them later.
There are many online tools that facilitate this process. If you’re looking for a webtool, try Inspiration, MindMeister, or another from this list. For iPads, try iBrainstorm, Ideament, or another from this list.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
8 Reasons for and 8 Against Revisiting Software in the Classroom
 I recently chatted with a tech coordinator on the East coast who asked about software alternatives to the webtools we were discussing. That surprised me. Usually, teachers want free, easily-accessible-from-anywhere webtools in place of expensive, installed software. When I asked why she had some excellent reasons:
I recently chatted with a tech coordinator on the East coast who asked about software alternatives to the webtools we were discussing. That surprised me. Usually, teachers want free, easily-accessible-from-anywhere webtools in place of expensive, installed software. When I asked why she had some excellent reasons:
No ads
Almost all free online tools and apps include advertising. I understand — someone has to pay the bill — but kids don’t understand how to ignore that glitz. All they see is a new toy. And besides the annoying ads, the developers constantly promote the paid version of the free apps. Again, kids don’t understand marketing.
You get the entire program
When you purchase software, you get the entire program. With online tools, you might get one or two levels of a few of the included games with the expectation that you will purchase more levels and more games. My most recent disappointment is Starfall. The mobile version of this wonderful online reading website is a very limited version of the original. To get the entire program requires multiple apps and significant in-app purchases.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
7 Innovative Writing Methods for Students
Knowledge is meant to be shared. That’s what writing is about–taking what you know and putting it out there for all to see. When students hear the word “writing”, most think paper-and-pencil, maybe word processing, but that’s the vehicle, not the goal. According to state and national standards (even international), writing is expected to “provide evidence in support of opinions”, “examine complex ideas and information clearly and accurately”, and/or “communicate in a way that is appropriate to task, audience, and purpose”. Nowhere do standards dictate a specific tool be used to accomplish the goals.
In fact, the tool students select to share knowledge will depend upon their specific learning style. Imagine if you–the artist who never got beyond stick figures–had to draw a picture that explained the nobility inherent in the Civil War. Would you feel stifled? Would you give up? Now put yourself in the shoes of the student who is dyslexic or challenged by prose as they try to share their knowledge.
When you first bring this up in your class, don’t be surprised if kids have no idea what you’re talking about. Many students think learning starts with the teacher talking and ends with a quiz. Have them take the following surveys:
- North Carolina State University’s learning style quiz
Both are based on the Theory of Multiple Intelligences, Howard Gardner’s iconic model for mapping out learning modalities such as linguistic, hands-on, kinesthetic, math, verbal, and art. Understanding how they learn explains why they remember more when they write something down or read their notes rather than listening to a lecture. If they learn logically (math), a spreadsheet is a good idea. If they are spatial (art) learners, a drawing program is a better choice.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
5 Tech Tools That Motivate Every Reader
 I love having guest posts on Ask a Tech Teacher because I always learn a lot. In this case, efriend and fellow educator, Jessica Sanders from WhooosReading.org, shares her favorite tools for kick-starting readers. I think you’ll like her choices:
I love having guest posts on Ask a Tech Teacher because I always learn a lot. In this case, efriend and fellow educator, Jessica Sanders from WhooosReading.org, shares her favorite tools for kick-starting readers. I think you’ll like her choices:
Not every student is motivated to read—as you, as an educator, know better than anyone else. Luckily, technology not only comes as second nature to the digital citizens in your classroom, but engages readers of every level, motivating them to read.
These five tech tools do exactly that, and can be used in almost any classroom environment or to encourage independent reading at home. Harness the power of peer-to-peer book recommendations and gamification to motivate your students to read more every day.
Nothing inspires students to read more than recommendations from their friends. Bookopolis harnesses that power by offering students a social reading community, where they can share book recommendations, write book reviews, and more.
Students can sign up alone, or with the help of their parent or teacher. Through the platform, students have a chance to uncover more of what they love or discover the kind of books they want to start reading.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
3 Apps to Build Solid Study Skills
It’s not enough to share information with students. Unless they have an eidetic memory, much of what they see/hear/taste/smell never reaches long term memory. For that, students require study. That includes note-taking and review in a variety of formats to touch the varied approaches to learning.
Here are three apps I find helpful with students. They are flexible, scalable, and as a group, address a variety of learning approaches students use. This includes traditional handwritten notes, collecting multimedia resources, and the ever-popular drill. Which is best for you?
 Papyrus
Papyrus
This is as close as you’ll get to pen-and-paper and be digital. No registration required and no ads. The start page is clear, uncluttered, with notes clearly listed. The menu bar is narrow and unobtrusive. Notes are taken on an infinite canvas as though it was a tablet of lined paper. You can add images, text, and audio files. Notes are saved in collections or singly which can then be exported as a PDF or an image.
Pros
Take notes with a finger, a stylus, or typed, even annotate PDFs (currently for an additional fee).
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
5 Best Practices for Digital Portfolios
Digital portfolios have become a critical part of today’s classroom. Why collate student work into clunky 3-ring binders that can only be one place at a time, are subject to damage and page loss, and are difficult to update when there are so many easy-to-use, intuitive digital versions:
- Blogs–Kidblogs, WordPress, Edublogs
- Digication

- Dropr
- Edusight–pictures of student work for a digital portfolio; free, app; online comprehensive picture
- Flipboard–a magazine format (iOS only)
- Google Drive
- Live Binders
- Three Ring--mini digital portfolio. Easy to use, quick, syncs with app–not as robust as others
- Wikispaces–or another wiki concept (PBWorks)
- WordPress–use blogs for e-porfolios
Each offers a unique collection of tools, differentiating for the diverse needs of today’s learners. How do you decide which is best for you? Start with the list of Best Practices for selecting and using digital portfolios. Consider the following:
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
5 Image Apps for your Classroom
Any child knows that a picture communicates differently than text. It’s not just quicker, it shares more detail more effectively. In seconds, our brain grasps a wide selection of data from the picture’s color, layout, design and draws conclusions. To do that with text requires lots of words, re-reading, extreme concentration, and scratching the head.
It’s no surprise research indicates the majority of students learn better if they see information. This includes graphic organizers, diagrams, mind maps, outlines–even pictures and art work.
Here are five image apps. One (or more) of these will be perfect for your classroom:
Canva
Free
1.8 million users have created over 15 million designs using Canva’s one million+ design templates (including font schemes, stock photographs, backgrounds, and illustrations–some free/some fee) to create cards, fliers, posters, newsletters, infographics, and more. Drag and drop project parts to personalize the design (see my Canva-created poster below). Edit photos using preset filters or advanced photo editing tools like brightness, contrast, saturation, tint, and blur. Save as a high-quality image or a printable PDF. Canva provides lots of graphic design video tutorials for even the most basic skill level. These are great for mature elementary age, Middle School, and High School students, as well as teachers.
Canva for education features 17+ lesson plans from some of the leaders in tech-in-ed. You can even sign in through Google Apps for Education. Canva not only works on iPads, but desktops and laptops.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
3 Lesson Plans to Teach Architecture in First Grade
 Here’s a great lesson plan with three activities well-suited to the discussion of architecture and design in 1st grade:
Here’s a great lesson plan with three activities well-suited to the discussion of architecture and design in 1st grade:
Review
Students complete three projects in two weeks to aid understanding of architecture, design, and three-dimensional thinking. They’ll experiment with spatially laying out a three-dimensional structure on a two-dimensional paper. When completed, they’ll discuss with neighbors while practicing good listening skills learned in class.
Start with a discussion of design. This includes size, shape, texture, proportion, scale, mass and color. We will apply these to rooms, buildings, and neighborhoods. Encourage students to think and analyze critically as they engage in learning.
In figures below, ask students which are two- or three-dimensions? How do they know?
[gallery ids="50170,50171,50172,50173,50164"]Design the Classroom
Visit Classroom Architect and demo how to design the classroom with drag-and-drop pieces (see figures below). Take suggestions from class on layout. Students must think about where tables and storage are relative to other items. This is an active learning lesson that encourages visual thinking. Develop a sample based on class input and show how to make corrections if necessary.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
8 Tech Tools to Get to Know Your Students for Back to School
The first day of class can be daunting. Students are curious about the new faces around them, intimidated–even frightened by the prospect of so many people they know nothing about. As a teacher, you might feel the same way. You knew everything about last year’s students, got excited when their baseball team won the playoffs, cried with them when a favorite pet passed away, cheered when they got an A in math. Those details–that intimate knowledge–helped you understand what motivated them so you could differentiate instruction to reach each of them where they were.
Now, you’re starting over. It would be easy to go around the room and have everyone introduce themselves, but you want the first-day ice-breaker to be more–enriching but fun, to set the tone for the rest of the year. You want students to quickly get comfortable with each other, bond as a group, without turning the classroom into a party room. And, you want an activity them haven’t done so many times in the past it’s boring.
One truth never changes: Students love talking about themselves. There’s no better ice breaker than one where students share information about themselves. There’s no better way to discover new friends than have a classmate understand perfectly what you’re saying about a tough soccer game because s/he too plays soccer.
Another truth: Kids love technology. This year, try a get-to-know-you that uses one of the many free online tech tools. How about these ideas:
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More










































