Tag: assessments
Measuring Up–the Key to Meeting State/National Standards
 Last year, only 61 percent of high school students who took the ACT English achievement test were deemed college-ready. In math, it was 41 percent. We teachers recognize it is our fiduciary responsibility to fulfill state and national education standards that prepare students for college or career. Many of us find students benefit greatly when the school employs curriculum-based assessments to measure progress. Why? Because by teaching, assessing knowledge, tracking progress, and personalizing to student needs, we can determine if students are accomplishing what they must to complete the work of learning.
Last year, only 61 percent of high school students who took the ACT English achievement test were deemed college-ready. In math, it was 41 percent. We teachers recognize it is our fiduciary responsibility to fulfill state and national education standards that prepare students for college or career. Many of us find students benefit greatly when the school employs curriculum-based assessments to measure progress. Why? Because by teaching, assessing knowledge, tracking progress, and personalizing to student needs, we can determine if students are accomplishing what they must to complete the work of learning.
Unfortunately, most textbooks offer no easy way to measure overall progress toward completing state or national standards, nor do they backfill for a lack of knowledge. Both of these are critical pieces to the successful accomplishment of learning goals.
This is where Mastery Education’s Measuring Up can help.
What is Measuring Up?
Measuring Up is a suite of tools that supplements any classroom curriculum by offering standards-based instruction, practice, assessment, and reporting customized to many state or national standards–with the singular goal of assisting students in meeting English Language Arts, Mathematics, and/or Science standards.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
Helping My Daughters Prepare for the ACT Exams
A few months ago, Jane Sandwood sent me a nice note. She’s a a freelance writer, editor and former tutor, homeschooler, and mother of two teenage daughters. She’d read my articles about preparing for SAT/ACTs and had a story of her own detailing how she helped her children prepare for their ACT. I think you’ll enjoy her experiences! 
As spring approaches, my eldest daughter Katherine, now in her junior year, is bracing herself for the upcoming ACT exams, while my youngest, Elizabeth, a sophomore, is getting ready for next year. I am a former tutor and for almost 10 years, I helped students prepare for both SATs and ACTs, relying heavily on tech tools and games to keep them motivated. Somehow, even students who needed the most help weren’t quite as challenging as my own daughters, and the lines between tutor and mom were often blurred, as is to be expected.
Different Learning Styles
Katherine and Elizabeth are just about as different as two people can be when it comes to their attitudes about school and their interests. Katherine, who wishes to be an actor, always took to her studies almost instinctively, since she was a child. She took great pride in handing in her homework neatly, took great pains to finish all her tasks, and was more of a rote learner than Elizabeth, who is more into writing, and who always took a more critical, analytical approach to her studies.
Elizabeth is naturally bright and quick, and has an enviable memory. She has always loved reading and has amassed quite a collection on her Kindle, yet is reticent to complete homework and has always had a strong aversion to maths. Because things tend to come easier to her, she is easily bored and far less disciplined than Kathy when it comes to homework and creating a study strategy. She also struggles with time management, often getting lost in a book or musical album and arriving to school without having completed home tasks.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
How to Prepare for the SAT
 Taking the Scholastic Aptitude Test (SAT) has become a right-of-passage for high school students as they leave formal education and enter the next phase of learning. Over seven million will take SAT tests in 2018 in January, March/April, May, June, October, November, or December. Some will take it for the first time; some for the umpteenth time. For many, it represents a last desperate attempt to qualify for the college of their dreams.
Taking the Scholastic Aptitude Test (SAT) has become a right-of-passage for high school students as they leave formal education and enter the next phase of learning. Over seven million will take SAT tests in 2018 in January, March/April, May, June, October, November, or December. Some will take it for the first time; some for the umpteenth time. For many, it represents a last desperate attempt to qualify for the college of their dreams.
In an earlier article, I focused on preparation for the essay portion of the SAT. This time, I’ll discuss some of the great online sites that help students prepare for the math and reading portions. I’ve based my selections on the following criteria:
- ease of use — accounts are easy to set up with access to both the site and materials quick and intuitive
- well-rounded — nicely differentiated tools that address varied student learning styles
- quantity and quality of available prep materials — materials are both in-depth and in a variety of formats (written, online, video, live/chat) with explanations of answers
- cost vs. value — free is nice but if students get good value for fee-based resources, that’s just as important
- time commitment — students can spend as much or little time as they have on any given day
Here are eleven options for SAT preparation, from my Top Five choices to six Honorable Mentions. All are easy to use, differentiated, up-to-date on the recent changes to the SAT, and represent a good investment of both time and money:
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
Innovative Ways to Encourage Writing
 Knowledge is meant to be shared. That’s what writing is about–taking what you know and putting it out there for all to see. When students hear the word “writing”, most think paper-and-pencil, maybe word processing, but that’s the vehicle, not the goal. According to state and national standards (even international), writing is expected to “provide evidence in support of opinions”, “examine complex ideas and information clearly and accurately”, and/or “communicate in a way that is appropriate to task, audience, and purpose”. Nowhere do standards dictate a specific tool be used to accomplish the goals.
Knowledge is meant to be shared. That’s what writing is about–taking what you know and putting it out there for all to see. When students hear the word “writing”, most think paper-and-pencil, maybe word processing, but that’s the vehicle, not the goal. According to state and national standards (even international), writing is expected to “provide evidence in support of opinions”, “examine complex ideas and information clearly and accurately”, and/or “communicate in a way that is appropriate to task, audience, and purpose”. Nowhere do standards dictate a specific tool be used to accomplish the goals.
In fact, the tool students select to share knowledge will depend upon their specific learning style. Imagine if you–the artist who never got beyond stick figures–had to draw a picture that explained the nobility inherent in the Civil War. Would you feel stifled? Would you give up? Now put yourself in the shoes of the student who is dyslexic or challenged by prose as they try to share their knowledge.
When you first bring this up in your class, don’t be surprised if kids have no idea what you’re talking about. Many students think learning starts with the teacher talking and ends with a quiz. Have them take the following surveys:
- North Carolina State University’s learning style quiz
Both are based on the Theory of Multiple Intelligences, Harold Gardner’s iconic model for mapping out learning modalities such as linguistic, hands-on, kinesthetic, math, verbal, and art. Understanding how they learn explains why they remember more when they write something down or read their notes rather than listening to a lecture. If they learn logically (math), a spreadsheet is a good idea. If they are spatial (art) learners, a drawing program is a better choice.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
Support English Learners with Micro-credentials from Digital Promise
 Education is changing. Again. This time, it’s not about iPads and Chromebooks; it’s 1:1 computing. More than 50% of teachers report they have one computer for every student (on average) and that changes for the better every year. Digital devices, be they iPads, laptops, Chromebooks, Macs, or PCs, give students access to endless amounts of web-based resources for research, inquiry, collaboration, sharing, and more. Schools are no longer reliant on years-old (or decades-old) textbooks written for the average student, whoever that is. It has become increasingly possible to personalize learning–adapt resources and assessments to student skills and needs and differentiate lessons that are pushed out to individual students or small groups (read: Shifting my Teacher Mindset with Micro-credentials).
Education is changing. Again. This time, it’s not about iPads and Chromebooks; it’s 1:1 computing. More than 50% of teachers report they have one computer for every student (on average) and that changes for the better every year. Digital devices, be they iPads, laptops, Chromebooks, Macs, or PCs, give students access to endless amounts of web-based resources for research, inquiry, collaboration, sharing, and more. Schools are no longer reliant on years-old (or decades-old) textbooks written for the average student, whoever that is. It has become increasingly possible to personalize learning–adapt resources and assessments to student skills and needs and differentiate lessons that are pushed out to individual students or small groups (read: Shifting my Teacher Mindset with Micro-credentials).
To do that requires competencies most teacher training programs never considered. As a result, an increasing number of schools are making micro-credentials a fundamental piece in their professional development plan.
What are Micro-credentials?
Micro-credentials are short, low-cost, focused, online classes that are self-paced and student-driven, offering competency-based recognition for skills educators want to learn to buttress their teaching.
Because they aren’t long tedious seminars, expensive college classes, or comprehensive certificate courses, they were ignored by administrators in the past. Not anymore.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
6 Options for Polls and Forms in Your Class
Collecting class data, asking for feedback on activities, and pushing out quizzes used to be laboriously accomplished by passing out paper documents, collecting them as they dribbled in, and then collating the data into a spreadsheet where you could sort and shake to come up with the useful information.
These days, all of those tasks are accomplished much more easily with one of the many free/fee webtools designed to create and curate information. Uses include but are not limited to: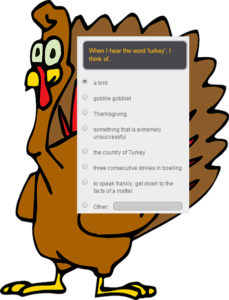
- volunteer sign ups
- feedback on events
- class enrollments
- donations and payments
- consent forms for school activities
- polls and surveys on upcoming or past events
- data on parents and students
- collection of student projects
- sign-ups for student class presentations
- signups for afterschool activities or summer classes
- registrations for a Professional Development workshop
- quizzes that are automatically evaluated providing students with their score and you with metrics
Besides the ease of use and their digital nature, students love forms because they are anonymous. This means when forms are used to collect feedback, input, and projects, students can participate at their own pace, as quietly as they’d like, with only the teacher being aware of their identity.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
12 Fresh Ways to Assess Student Learning
 Assessing student learning used to be as simple as giving a test that consisted of multiple choice, True/False, short answer, and/or essay. How many answers students got right told the teacher how much they knew. No need to look further. Simply grade, record, and move on to the next chapter.
Assessing student learning used to be as simple as giving a test that consisted of multiple choice, True/False, short answer, and/or essay. How many answers students got right told the teacher how much they knew. No need to look further. Simply grade, record, and move on to the next chapter.
Educators have come to realize that there are lots of reasons why a test score doesn’t reflect student knowledge. Maybe the student had a bad day; maybe s/he isn’t good at memorizing (and the test was mostly memorized facts); maybe education researchers are right that doing well on tests isn’t a predictor of student success.
Tossing tests makes a teacher’s job more difficult. I’ll stipulate to that. Habits, templates, and routines are much easier than reinventing the assessment wheel but a tool that results in passionate students committed to lifelong learning gets my attention.
That’s what the next twelve options are: assessment strategies that inspire student interest and allow them to share what they know in ways compatible with their personal communication style. These can be used formatively or summatively and can be created by teachers or students-as-teachers. Decide what works best for your circumstances. The uniting characteristics are that all assess:
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
How NOT to Assess Student Writing
 In my school, every teacher assesses writing. Even in the tech lab, which is my purview, I provide mini-how-to-write lessons before tech projects that include writing. That’s not just for essays or reports but slideshows, blog posts, comments in forums, and more. I remind students of the five-paragraph essay, synonyms, plan-revise-edit-rewrite, persuasive essays, letter writing, or whatever fits the day’s lesson.
In my school, every teacher assesses writing. Even in the tech lab, which is my purview, I provide mini-how-to-write lessons before tech projects that include writing. That’s not just for essays or reports but slideshows, blog posts, comments in forums, and more. I remind students of the five-paragraph essay, synonyms, plan-revise-edit-rewrite, persuasive essays, letter writing, or whatever fits the day’s lesson.
This connected teaching approach is consistent with most modern pedagogy. Writing is no longer treated as a stand-alone skill, rather a tool students use to provide evidence of their knowledge. If I use Common Core as an example, here’s what these Standards call out as important about writing (slightly rephrased from the Anchor Standards):
- Write arguments to support claims in an analysis of substantive topics using valid reasoning and relevant and sufficient evidence.
- Write informative/explanatory texts to examine complex ideas clearly and accurately through the effective selection, organization, and analysis of content.
- Write narratives to develop experiences using effective techniques, well-chosen details, and well-structured event sequences.
- Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience.
- Develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach.
- Use technology to produce and publish writing.
- Conduct research based on focused questions that demonstrate understanding of the subject.
- Gather relevant information, assess the credibility and accuracy of each source, and integrate the information while avoiding plagiarism.
- Draw evidence from literary or informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research.
- Write routinely for a range of tasks, purposes, and audiences.
Note that nowhere do the Standards mention handwriting, word processing tools, editing typos, or general technology skills. Why? Because achieving the Standards transcends the media with which you write. Whether that’s paper-and-pencil or word processing, audio, comics, or video, the goal is to communicate ideas.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
What is Standards-based Grading?
 How many times have you experienced teachers who based report card grades on how well students complete classwork, homework, and quizzes? They mistakenly conflate these exemplars with learning. For example, a book report may require a certain number of written (or typed) pages or paragraphs rather than evidence that the student drew conclusions and summarized knowledge.
How many times have you experienced teachers who based report card grades on how well students complete classwork, homework, and quizzes? They mistakenly conflate these exemplars with learning. For example, a book report may require a certain number of written (or typed) pages or paragraphs rather than evidence that the student drew conclusions and summarized knowledge.
That’s changing. Today, many educators want to not only evaluate progress at a point in time but optimize that against the ongoing standards their school mission is built on such as Common Core, International Baccalaureate, NGSE, or TEKS.
What is Standards-based Grading
To accomplish this, many schools and Districts have turned to Standards-based Grading. According to Tomlinson and McTighe, standards-based grading (SBG) “measures student proficiency on well-defined course objectives.” This means students have clear guidelines for how to define success over time, making it easy for all stakeholders in a student’s learning to determine if they are accomplishing what must be done for college and career. It de-emphasizes subjectivity by providing an objective delineation of requirements.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
169 Tech Tip #98: 13 Tips for Email Etiquette
 In these 169 tech-centric situations, you get an overview of pedagogy—the tech topics most important to your teaching—as well as practical strategies to address most classroom tech situations, how to scaffold these to learning, and where they provide the subtext to daily tech-infused education.
In these 169 tech-centric situations, you get an overview of pedagogy—the tech topics most important to your teaching—as well as practical strategies to address most classroom tech situations, how to scaffold these to learning, and where they provide the subtext to daily tech-infused education.
Today’s tip: #98–13 Tips for Email Etiquette
Category: Email
Sub-category: Assessment
Here’s a poster with 13 email etiquette tips to share with new users:
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More








































