Tag: pedagogy
Understanding By Design — What’s That Even Mean?
 Created by Grant Wiggins and Jay McTighe, Understanding by Design (UbD) is a lesson planning approach that visualizes the end result (what students should understand) to better select learning activities (the path that will get students there). Tens of thousands of educators use it for unit and course planning; hundreds of districts and schools use it as the basis for their curricula. Look at who has adopted UbD:
Created by Grant Wiggins and Jay McTighe, Understanding by Design (UbD) is a lesson planning approach that visualizes the end result (what students should understand) to better select learning activities (the path that will get students there). Tens of thousands of educators use it for unit and course planning; hundreds of districts and schools use it as the basis for their curricula. Look at who has adopted UbD:
- the College Board, to guide the revision of its Advanced Placement (AP) subject matter courses and for the development of its courses AP Seminar and AP Research
- the framework for the national curriculum in the Philippines and Puerto Rico
- the state of Massachusetts, for its Race to the Top federal grant program to create more than one hundred exemplary units and associated classroom videos
- the Next Generation Arts Standards
Additionally, the two largest textbook publishers, Pearson and McGraw-Hill, use the UbD framework in many of their textbooks and programs, similar to this example from Pearson’s biology curriculum.
Share this:
How to Incorporate Mindfulness into Your Class
 Students learn best when they are relaxed, happy, and feeling loved. It is challenging to include those characteristics in classes when you are concurrently trying to achieve school goals, comply with curriculum timelines, juggle parent concerns, and blend your lessons with those of colleagues.
Students learn best when they are relaxed, happy, and feeling loved. It is challenging to include those characteristics in classes when you are concurrently trying to achieve school goals, comply with curriculum timelines, juggle parent concerns, and blend your lessons with those of colleagues.
This is where mindfulness becomes important. It reminds teachers that the fulcrum for learning is the student’s emotional well-being.
Let’s back up a moment: What is mindfulness? Buddha once said:
“Do not dwell in the past, do not dream of the future, concentrate the mind on the present moment.”
If that’s the plan, mindfulness is the path. It teaches students how to quiet themselves — get to a place where their mind is settled sufficiently to pay full attention to the task at hand. Experts offer many suggestions for incorporating mindfulness into your classroom experience. Consider:
- pause and take a deep breath before beginning an activity or in the middle of performing it
- reflect on an activity as a group
- reflect on the student’s own experiences and background and how that relates to the topic
Delving into these rudimentary steps isn’t the goal of this article (find more about that in Janelle Cox’s TeachHUB article). Today, I want to show you how to take the incorporation of mindfulness into your classes to the next level. Here are five ideas:
Share this:
169 Tech Tip #126–7 Tips to Differentiate with Tech
 In these 169 tech-centric situations, you get an overview of pedagogy—the tech topics most important to your teaching—as well as practical strategies to address most classroom tech situations, how to scaffold these to learning, and where they provide the subtext to daily tech-infused education.
In these 169 tech-centric situations, you get an overview of pedagogy—the tech topics most important to your teaching—as well as practical strategies to address most classroom tech situations, how to scaffold these to learning, and where they provide the subtext to daily tech-infused education.
Today’s tip: #126: 7 Tips to Differentiate with Tech
Category: Differentiation
Sub-category: Teaching, Pedagogy
Here are seven ways to differentiate instruction every day:
- While some students take their time to carefully finish a project as suits their learning style, others slam through the steps, looking for ‘what’s next’. Both are fine. Have a lot of authentic activities going on in your classroom so students are encouraged to work at their own pace. Let them self-manage their education. Be clear about your expectations, and then trust them to find their way. Have links on the class internet start page for organic learning like keyboarding practice and sponge websites that tie into subject area inquiry.
- Let students communicate ideas with not only text, but layout, color, and images. These can be graphic organizers like Venn Diagrams or pyramids, or an infographic made in ly. Let students
- Show students how to add pictures, borders, and fonts. Some students will tolerate the words to get to the decorating.
- Use online tools like Discovery Education’s Puzzle Maker to review concepts. Move away from rubrics and study guides. Anything that gamifies learning will go down easier with students. They are digital natives so let them learn in a more natural way.
- In fact, gamify anything possible. There are an amazing number of high-quality simulations that teach through games–Minecraft,iCivics, Mission US, Lemonade Stand. Here’s a long list. There’s probably one for every subject. Take advantage of them.
- If students aren’t excited by the tools and widgets you offer, let them suggest their own. If they can make the argument for it, let them use it.
- Always offer do-overs. I call them ‘Mulligans’. In a differentiated classroom, let students redo an assignment. What if they didn’t understand? Or were sick? How does trying harder defeat education’s goal of learning? With technology, all students do is open their project and continue work based on your feedback. That’s cool. Rest assured: When you offer this in your classroom, most students won’t take you up on it. It’s too outside-the-box. You won’t be deluged with double the work. But, be happy if you are.
Share this:
Why is PBL So Popular in Schools?
 The norm in classrooms across the country used to be the teacher at the front lecturing, students taking notes which they then memorized for a summative test that decided their grade. Because the teacher was the expert, students learned at their feet, absorbing knowledge from the person who knew everything. In the early 1900’s, John Dewey suggested the education focus be switched to students when he introduced “learning by doing”, today referred to as Project-based Learning (PBL).
The norm in classrooms across the country used to be the teacher at the front lecturing, students taking notes which they then memorized for a summative test that decided their grade. Because the teacher was the expert, students learned at their feet, absorbing knowledge from the person who knew everything. In the early 1900’s, John Dewey suggested the education focus be switched to students when he introduced “learning by doing”, today referred to as Project-based Learning (PBL).
“All genuine learning comes through experience.” – John Dewey
This approach to learning has been successfully employed for more than one hundred years. Throughout modern history, PBL in the form of apprenticeships has been a valued and iconic approach to preparing children for adult jobs. Even before that, young chimpanzees learn to eat from termite mounds by mimicking what they see adults do — “learning by doing”.
What is PBL?
Project-based learning (PBL) asks teachers to act as facilitators, not lecturers, guiding students to find the necessary answers for the theme-related project they are completing. Students are no longer passive listeners who expect the teacher to have all the answers. In fact, students take charge of their own learning as they make choices about how to learn, plan how it should be done, solve their own problems, and present the results to fellow learners.
Share this:
How to Blend DoK into Lesson Plans without a Comprehensive Rewrite
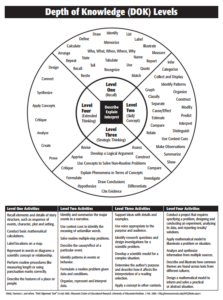 I recently got a question from a reader asking how the lessons in my K-8 curriculum supported Dr. Norman Webb’s Depth of Knowledge philosophy — an integral concept to her school’s mission. It got me thinking about lesson plans in general — how far we’ve come from lecture-test-move on. Now, exemplary teachers focus on blending learning into the student’s life knowledge base with the goal of building happy, productive adults. There are several concepts that address this reform in teaching (such as Art Costa’s Habits of Mind, Bloom’s Taxonomy, the Hess Cognitive Rigor Matrix, or the tech-oriented SAMR Model). Depth of Knowledge (DoK) is arguably the most thorough with its four concise levels, each supported by a collection of words that contribute to delivering content at that level. Like the SAMR Model, involvement grows with each level from a basic recall of knowledge to the ability to use that information in new circumstances.
I recently got a question from a reader asking how the lessons in my K-8 curriculum supported Dr. Norman Webb’s Depth of Knowledge philosophy — an integral concept to her school’s mission. It got me thinking about lesson plans in general — how far we’ve come from lecture-test-move on. Now, exemplary teachers focus on blending learning into the student’s life knowledge base with the goal of building happy, productive adults. There are several concepts that address this reform in teaching (such as Art Costa’s Habits of Mind, Bloom’s Taxonomy, the Hess Cognitive Rigor Matrix, or the tech-oriented SAMR Model). Depth of Knowledge (DoK) is arguably the most thorough with its four concise levels, each supported by a collection of words that contribute to delivering content at that level. Like the SAMR Model, involvement grows with each level from a basic recall of knowledge to the ability to use that information in new circumstances.
Here are general details about Webb’s DoK:
- With Webb’s DoK chart, not only can you figure out how to teach a subject more deeply and expect students to demonstrate complex understanding, but teachers can evaluate where students are in the four-step process starting at the rote application of knowledge to its synthesization from various sources that is then transferred to other uses.
- Level One: Identify details in the text, specific facts that result in a ‘right’ answer. Tasks that require Level One thinking include words like memorize, state, and recognize.
- Level Two: Show a relationship between an idea in the text and other events. ‘How’ and ‘why’ are good questions to bump an activity into Level Two. Tasks that require Level Two thinking include words like compare, infer, and interpret.
- Level Three: Analyze and draw conclusions about the text. Support conclusions with details. Use a voice that is appropriate to the purpose, task, and audience. Tasks that require Level Three thinking include words like hypothesize, differentiate, and investigate.
- Level Four: Extend conclusions and analysis (which might be the result of Level three) to new situations. Use other sources to analyze and draw conclusions. Tasks that require Level Four thinking include words like connect, analyze, and prove.
- As Dr. Karin Hess says, DoK is not about difficulty, it’s about complexity. Level One may be difficult for some students, but it isn’t complex. They may memorize a calculus formula (which I’ll stipulate is beyond difficult), but it doesn’t represent rigorous thinking. That happens in Level Four’s application to the real world.
- For DoK’s Level One and Two, there are usually right answers. That’s not true in Levels Three and Four.There, it’s about higher-order thinking.
- DoK is not a taxonomy (like Bloom’s). Rather, it itemizes ways students interact with knowledge.
- To work at a Level Three or Four requires foundation. Show students how to accomplish Level One and Two goals first.
With that in mind, here are seven steps to transform your current lesson plan into one aligned with DoK guidelines:
Share this:
Use the SAMR Model to Spearhead Technology in Your Classroom
 This is a question I get often from teachers: Technology is always an extra layer of work in my classroom. How can I blend it into what I already do without taking time I don’t have? When I first addressed this issue fifteen years ago, it was all about replacing traditional classroom tools with one on a computer. For example, book reports were typed on the computer instead of handwritten, or math facts were practiced with a math game instead of flash cards. But that quickly became cumbersome. Teachers didn’t know how to use the digital tools and there was never enough training to untip that balance. At the end of the day, paper-and-pencil was easier, faster, and perfectly understood. Soon, even the most stalwart tech-infused teachers discovered it was just as effective to use traditional tools and pull out the tech stuff for special occasions.
This is a question I get often from teachers: Technology is always an extra layer of work in my classroom. How can I blend it into what I already do without taking time I don’t have? When I first addressed this issue fifteen years ago, it was all about replacing traditional classroom tools with one on a computer. For example, book reports were typed on the computer instead of handwritten, or math facts were practiced with a math game instead of flash cards. But that quickly became cumbersome. Teachers didn’t know how to use the digital tools and there was never enough training to untip that balance. At the end of the day, paper-and-pencil was easier, faster, and perfectly understood. Soon, even the most stalwart tech-infused teachers discovered it was just as effective to use traditional tools and pull out the tech stuff for special occasions.
What happened? How did such a good idea go so wrong? The problem was four-fold:
- students didn’t have the technology foundation to smoothly incorporate digital tools into projects. Too often, the effort to provide evidence of learning suffered as students (and teachers) became mired in efforts to get the technology to work. Where is the tool? How do you do **? Why is the program not working?
- teachers didn’t have training in the tools. Even schools that made herculean efforts to train teachers in technology found themselves flailing. Even teachers who understood the tool would struggle with the inadequate infrastructure, the undependability of the technology itself, and the non-intuitive nature of so many of the programs they wanted to use. As a result, they used tools they understood rather than those best-suited for the project and learning.
- projects always–really, always–took longer using technology than the traditional low-tech approach.
- school infrastructure often struggled to support the exciting plans that tech-savvy teachers wanted to try. Computers froze or the network became over-burdened or the internet went down just as students required them the most. The money required to fix these problems was measured in the thousands of dollars–tens of thousands. Too many schools just didn’t have that budget.
Share this:
How to Create a Tech-based Curriculum Using the SAMR Model
 This is a question I get often from teachers: How do I teach my state/national/international curriculum using technology? When I first addressed this issue about fifteen years ago, there weren’t any tools to make this happen. In fact, I ended up writing my own project-based technology curriculum (now in its fifth edition). I wanted a curriculum that scaffolded learning year-to-year, blended into the school academic program, could be re-formed to apply to any academic topic, differentiated for varied student learning style, and was age-appropriate for the needs of the digital natives populating my classroom. Everything I found through traditional sources was skills-based, undifferentiated, and relied on programs that have always been around rather than the ones that incited student passion.
This is a question I get often from teachers: How do I teach my state/national/international curriculum using technology? When I first addressed this issue about fifteen years ago, there weren’t any tools to make this happen. In fact, I ended up writing my own project-based technology curriculum (now in its fifth edition). I wanted a curriculum that scaffolded learning year-to-year, blended into the school academic program, could be re-formed to apply to any academic topic, differentiated for varied student learning style, and was age-appropriate for the needs of the digital natives populating my classroom. Everything I found through traditional sources was skills-based, undifferentiated, and relied on programs that have always been around rather than the ones that incited student passion.
The most difficult part was convincing colleagues that 2nd graders couldn’t write a book report in MS Word until they understood toolbars, keyboarding basics, enough digital citizenship to research effectively online, and how to solve the never-ending-but-repetitive tech problems they surely would face during their work.
Overall, it took a year to curate teacher needs, evaluate what skills were required to accomplish them, and then blend them into a tech program that optimized learning for the particular age group.
Before I disclose my secret formula, let’s assess where you are–right now–in your technology integration efforts. Dr. Ruben Puentedura developed the popular SAMR model as a way for teachers to evaluate how they are incorporating technology into their instructional practice. Here’s how it works:
Substitution
Tech acts as a direct tool substitute with no functional change.
This is a great starting point. Look at what you’re doing in your lesson plans and consider what tech tools could replace what you currently use. For example, if you make posters to discuss great inventors, could you use an online tech tool like Glogster or Canva?
Augmentation
Tech acts as a direct tool substitute with functional improvement.
Share this:
A Conversation about Keyboarding, Methods, Pedagogy, and More
Dr. Bill Morgan and I have engaged in several months of spirited conversation about keyboarding, pre-keyboarding, and how it can best serve students. Bill is the brilliant creator of the PreKeys Pond and giant keyboards for classrooms. His experience teaching keyboarding often informs me in my art as I adapt to the ever-changing needs of the students in my classes. I’ve hosted Bill before on Ask a Tech Teacher (see this article on Preparing Young Students for Home Row Keyboarding: An Unplugged Approach). Today, I’m going to share random thoughts from a collection of our emails. Bill’s thoughts are in italics and mine in red and parentheses:
I have questions for the creators of Ratatype.com. They seem to be British since they use the term centimeters to refer to how close the keyboard and screen ought to be to the student. Of course, most of the world outside of the USA refers to centimeters instead of inches! I also want to thank Ratatype for clocking me at 97 wpm on the pretest. (🙂)
When typing, imagine the location of the symbol on the keyboard.
(I like that too. I need to incorporate more visual learning into my keyboard instruction).
Share this:
Digital Literacy–What is it?
‘Digital literacy’ is one of those buzz words floated by experts as being granular to 21st century students. It’s everywhere, on everyone’s tongue, but figuring out what it means can be daunting. ‘Literacy’ is simple: the ability to read and write–so ‘digital literacy’ should be achieving those goals digitally.
Not that simple. Here are a few of the definitions I found:
“the ability to find, evaluate, utilize, share, and create content using information technologies and the Internet.“.
–Cornell University
“the ability to use digital technology, communication tools or networks to locate, evaluate, use and create information”
–Digital Strategy Glossary of Key Terms
“the ability to understand and use information in multiple formats from a wide range of sources when it is presented via computers:
–Paul Gilster, Digital Literacy
“a person’s ability to perform tasks effectively in a digital environment… includes the ability to read and interpret media, to reproduce data and images through digital manipulation, and to evaluate and apply new knowledge gained from digital environments
–Barbara R. Jones-Kavalier and Suzanne L. Flannigan: Connecting the Digital Dots
Philosophically, these are all good definitions, but after fifteen years teaching K-8 technology and grad school, I know ‘digital literacy’ is much more complicated than a couple of sentences, especially when we’re talking about students baptized in iPads and smartphones. Here are the eight transformative skills required of the digitally-literate student:
 Basic tools
Basic tools
Digital literacy implies the same reading-writing skills, but without paper, pencils, books, or lectures. It’s purpose-built and student-driven. As a teacher, you’ll want to provide the following:
- digital devices–such as laptops, iPads, Chromebooks, or desktops, for daily use
- a digital class calendar–with due dates, activities, and other events
- an annotation tool (like Acrobat, Notability, or iAnnotate), to take notes
- a class internet start page–to curate websites, widgets, and other digital tools used for learning
- a backchannel device–to assess student learning while it’s happening (with tools such as Socrative, Today’s Meet, or Google Apps)
- a class website or blog–to share class activities with parents and other stakeholders
- student digital portfolios–to curate and collect student work for viewing and sharing
- student email–or some method of communicating quickly with students outside class time. This can be messaging, Twitter, or a dedicated forum
- vocabulary tool–so students can quickly decode words they don’t understand in their reading. Make this dictionary tool easily accessible from any digital device being used.
Share this:
Let’s Talk About Habits of Mind
 Pedagogic experts have spent an enormous amount of time attempting to unravel the definition of ‘educated’. It used to be the 3 R’s–reading, writing, and ‘rithmetic. The problem with that metric is that, in the fullness of time, those who excelled in the three areas weren’t necessarily the ones who succeeded. As long ago as the early 1900’s, Teddy Roosevelt warned:
Pedagogic experts have spent an enormous amount of time attempting to unravel the definition of ‘educated’. It used to be the 3 R’s–reading, writing, and ‘rithmetic. The problem with that metric is that, in the fullness of time, those who excelled in the three areas weren’t necessarily the ones who succeeded. As long ago as the early 1900’s, Teddy Roosevelt warned:
“C students rule the world.”
It’s the kids without their nose in a book that notice the world around them, make connections, and learn natively. They excel at activities that aren’t the result of a GPA and an Ivy League college. Their motivation is often failure, and taking the wrong path again and again. As Thomas Edison said:
“I have not failed. I’ve just found 10,000 ways that won’t work.”
Microsoft founder, Bill Gates, and Albert Einstein are poster children for that approach. Both became change agents in their fields despite following a non-traditional path.









































