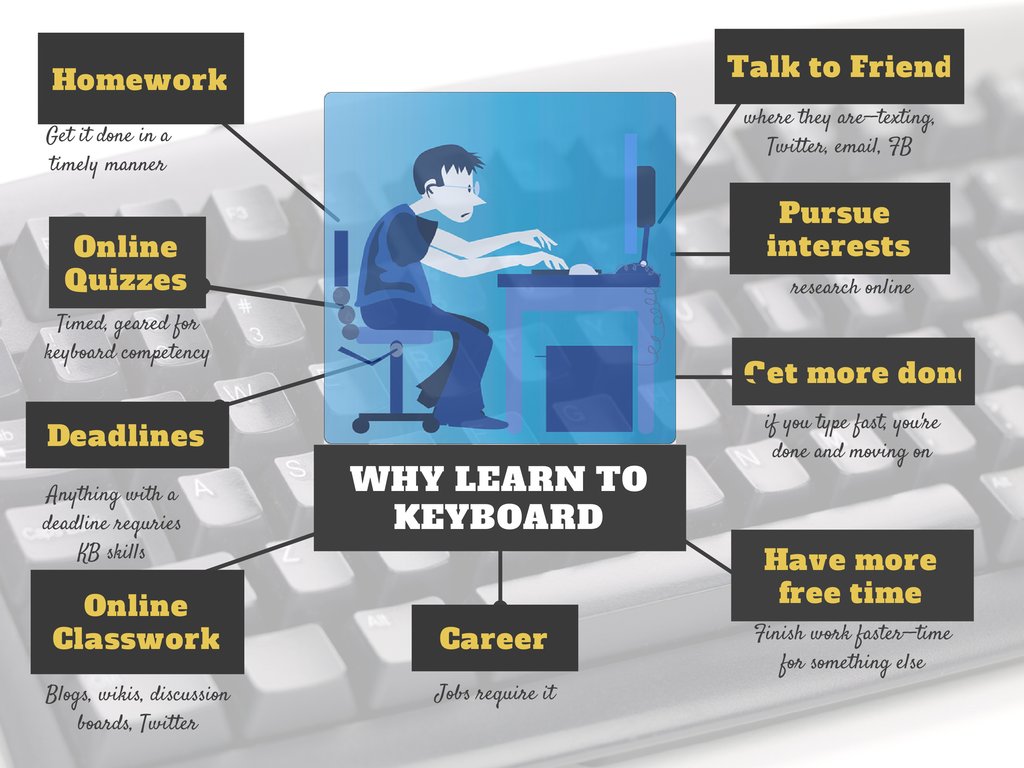
Category: 6th grade
Dear Otto: What are Common Core keyboarding standards?
 Dear Otto is an occasional column where I answer questions I get from readers about teaching tech. If you have a question, please complete the form below and I’ll answer it here. For your privacy, I use only first names.
Dear Otto is an occasional column where I answer questions I get from readers about teaching tech. If you have a question, please complete the form below and I’ll answer it here. For your privacy, I use only first names.
Here’s a great question I got from Lani :
I am trying to set up my curriculum map for 2013-14, for preK-8. This is the first year I will be actually using the lab f/t…I hope, along with library skills. I purchased several of the structured learning books & your blog has been amazing! My question, you mentioned that keyboarding is part of the CC…45wpm minimum, by end of 8th grade. I have looked at the CC State Standards, but cannot find this or any tech standards. Can you share where this is? I have new administration coming & would like to be prepared! Thank you.
- Keyboarding is addressed tangentially–saying students must be able to type *** pages in a single sitting (see CCSS.ELA-Literacy.W.4.6 for example. The ‘pages in a single sitting’ starts in 4th grade and continues through 6th where it’s increased to three–see CCSS.ELA-Literacy.W.6.6)
- By 3rd grade, Common Core also discusses the use of keyboarding to produce work, i.e., CCSS.ELA-Literacy.W.3.6 which specifically mentions ‘use technology to produce and publish writing (using keyboarding skills)’
- The keyboarding requirement that is giving teachers across the continent heartburn is that keyboarding will be required to take Common Core Standards assessments (a year off except where Districts are testing this eventuality).
It’s worth noting that CC standards are progressive–students are expected to learn material, transfer that knowledge to the next grade level where they show evidence of having learned it by using it and building on it. Therefore, the notation to ‘produce and publish writing using keyboarding skills’ in 3rd grade carries into all successive grade.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
How to Instill Digital Citizenship in Students
 What is a parent’s greatest fear that first day they drop their precious child at kindergarten? You might think it’s whether they’ll get along with new friends or handle academic pressures. Or even that their eyes will be opened to the vastness of the Universe and no longer see their parents as the Answer to Everything.
What is a parent’s greatest fear that first day they drop their precious child at kindergarten? You might think it’s whether they’ll get along with new friends or handle academic pressures. Or even that their eyes will be opened to the vastness of the Universe and no longer see their parents as the Answer to Everything.
Those are frightening, and might be ranked in the top ten–or even five–but today, the biggest concern is how to protect an innocent from the pernicious onslaught of the technology that grows like mold over every part of the education landscape. Will that trusting child be cyberbullied? Will they see stuff they shouldn’t on school websites? Will a predator find them from a naive contact online? And what about classmates–will they share bad websites found by older siblings?
It may surprise you that this scenario also keeps teachers awake at night, especially new teachers. What if they fail to protect their charges from this violent, dark online world? I remember second grade life cycle reports. I taught students how to search online images for pictures of each stage in a bug’s development, save them to student network folders, and then proudly insert them in the report. Students would find authentic and exciting pictures of ‘ladybugs’ and ‘pupae’ and ‘preying mantis larvae’ and ‘chicks’–
Chicks! That turned out to be a lousy search term. I’d warn students to search ‘baby chickens’ instead, but always, for one child each year, it wouldn’t work and–according to their parents–were permanently damaged by the pictures that popped up. They’d have nightmares. Their personalities would forever tilt to the dark side because of that picture–at least.
Truth, all stakeholders do their best, but stuff happens. If not in the classroom, at a friend’s house whose parents aren’t as vigilant as they could be, or on an iPad during library time. Educational best practices used to insist on protecting children from those eventualities, minimize exposure by unplugging kids as much as possible. That’s not the case any more. Even if we unplug them at the school house door, they plug right back in the moment they are away from the classroom. Our job as educators is to stare into the abyss of the unknown and educate: Teach these digital natives how to not just survive but thrive in the digital world.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
Do you like Online Training?
I have just started working with an online teacher training group called Curriculum Study Group. We offer online training to teachers via Google Hangouts, YouTube, instant feedback, and lots of collaborative learning. I am very excited to be part of this venture…
…but I must confess, before I joined, I wondered if teachers would be comfortable hanging out with like-minded professionals for an hour a week? Well, my good friend Amy over at CSG sent me this survey run by Project Tomorrow, a nonprofit group based in Irvine, Calif (my backyard). It seems they had the same question so did a poll. Here are the results:
What’s the take-away: Yes, across the board, principals and teachers are comfortable with online training.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
Book Review: K-8 Keyboard Curriculum
K-8 Keyboard Curriculum: The Essential Guide to Teaching Keyboarding in 45 Minutes a Week
You may think it impossible to find an effective keyboarding curriculum for the skimpy forty-five minutes a week you can devote to keyboarding. You teach what you can, but it always seems to be the same lessons—hands on home row, good posture, eyes on the copy. You wonder if it’s making a difference, or if it matters.
Yes, it does and there is a way. It requires a plan, faithfully executed, with your eye relentlessly on the goal, but if you commit, it works. In this book, The Essential Guide to Teaching Keyboarding in 45 Minutes a Week: a K-8 Curriculum, I’ll share a unique keyboarding curriculum for K-8 that I’ve seen work on thousands of students. The book includes:
- A summary of the literature
- Answers to the most-asked questions like ‘Can youngers learn to keyboard—and should they?’
- The importance of the teacher to early keyboarders
The K-8 curriculum includes a lot more variety than keyboard exercises on installed software. Here’s a rundown of the pieces used:
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
Book Review: K-8 Digital Citizenship Curriculum
Education has changed. No longer is it contained within four classroom walls or the physical site of a school building. Students aren’t confined by the eight hours between the school bell’s chimes or the struggling budget of an underfunded program.
Now, education can be found anywhere, by collaborating with students in Kenya or Skyping with an author in Sweden or chatting with an astrophysicist on the International Space Station. Students can use Google Earth to take a virtual tour of a zoo or a blog to collaborate on a class project. Learning has no temporal or geographic borders, available 24/7 from wherever students and teachers find an internet connection.
This vast landscape of resources is available digitally, freely, and equitably, but before children begin the cerebral trek through the online world, they must learn to do it safely, securely, and responsibly. This conversation used to focus on limiting access to the internet, blocking websites, and layering rules upon rules hoping (vainly) that students would be discouraged from using this infinite and fascinating resource.
It didn’t work.
Best practices now suggest that instead of protecting students, we teach them to be good digital citizens, confident and competent in the use of the internet.
This 70-page text (click for a peek inside) is your guide to what our children must know at what age to thrive in the community called the internet. It’s a roadmap for blending all the pieces into a cohesive, effective student-directed cyber-learning experience that accomplishes ISTE’s general goals to:
-
- Advocate and practice safe, legal, and responsible use of information and technology
-
- Exhibit a positive attitude toward using technology that supports collaboration, learning, and productivity
- Demonstrate personal responsibility for lifelong learning
- Exhibit leadership for digital citizenship
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
24 Keyboarding Websites for Summer
Did you promise that this summer, your child would learn to type with more than two fingers, keep his eyes off his hands, and learn to like keyboarding? Your teachers consider that important–Common Core requires
 students type between 1-3 pages at a sitting without giving up from boredom, frustration, fatigue. To do that requires a knowledge of where the keys are on the keyb oard and what habits faciliate speedy, accurate typing.
students type between 1-3 pages at a sitting without giving up from boredom, frustration, fatigue. To do that requires a knowledge of where the keys are on the keyb oard and what habits faciliate speedy, accurate typing.
It doesn’t have to be rote drills, drudgery. There are a lot of options that make it fun. Here are 32. I think they’ll find a few they like:
- ABCYa–Keyboard challenge—grade level
- Alphabet rain game
- Barracuda game
- Big Brown Bear
- Bubbles game
- Dance Mat Typing
- Finger jig practice game
- Free typing tutor
- GoodTyping.com
- Keyboard practice—quick start
- Keyboarding practice
- Keyboarding—lessons
- Keyboarding—more lessons
- Keyboarding—must sign up, but free
- Keyboarding—quick start
- Keybr–Online practice
- NitroTyping
- Online typing lessons — more
- Touch Typing Progressive Program
- TuxTyping
- Typing Club
- Typing Defense—fun word practice
- TypingTest.com
- TypingWeb.com—a graduated course
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
12 Great Simulations to Gamify Your Class
Here are 15 websites I’ve found that do an excellent job of using games to promote critical thinking, problem solving skills, and learning:
- Bridge Builder—learn how to design and test bridges
- Coffee Shop—run a coffee shop business
- iCivics—experience what it means to be part of a democracy
- Lemonade Stand—run a lemonade stand business
- Making History: The Great War—WWI strategy game
- Minecraft (links to MinecraftEdu—fee required)
- Mission US––students role play the American Revolution or the Civil War
- Past/Present—life as an American immigrant in the early 1900’s
- Science simulations—lots of choices at 7th grade level
- Second Life—simulates just about anything if you can find it
- SimTower—learn how to run a skyscraper as a business
Suggestions for using Bridge Builder:
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
Dear Otto: Any Ideas for Tech Ed Benchmark Assessments?
 Dear Otto is an occasional column where I answer questions I get from readers about teaching tech. If you have a question, please complete the form below and I’ll answer it here. For your privacy, I use only first names.
Dear Otto is an occasional column where I answer questions I get from readers about teaching tech. If you have a question, please complete the form below and I’ll answer it here. For your privacy, I use only first names.
Here’s a great question I got from Lisa and Tamma:
My district is asking us to create assessments. I was wondering what you have included in them and how/when you administer them. Thanks!
Hi Lisa and Tamma
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
Dear Otto: How Do I Teach Citations?
 Do you have a tech question?[/caption]
Do you have a tech question?[/caption]
Dear Otto is an occasional column where I answer questions I get from readers about teaching tech. If you have a question, please complete the form below and I’ll answer it here. For your privacy, I use only first names.
Here’s a great question I got from Mary:
Based upon the Common Core expectations, how should we have students in grade 3-4 and 5-6 cite sources for research?
There is no easier way to teach citations than using an online citation creator:
Plug the information in on your SmartScreen to show students how it is done, and let the citation creator do the rest. Take time to explain the importance of each entry so students understand. This is fundamental to molding digital citizens out of the wild digital natives who enter your classroom. Help them understand the responsibilities that go hand-in-hand with the rights they acquire by accessing information on the internet.
Here’s an example using EasyBib:
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
Now Available: K-8 Digital Citizenship Curriculum
Digital Citizenship Curriculum for K-8 (print or digital)
Why do teachers need to teach Digital Citizenship?
Education has changed. No longer is it contained within four classroom walls or the physical site of a school building. Students aren’t confined by the eight hours between the school bell’s chimes or the struggling budget of an underfunded program.
Now, education can be found anywhere, by collaborating with students in Kenya or Skyping with an author in Sweden or chatting with an astrophysicist on the International Space Station. Students can use Google Earth to take a virtual tour of a zoo or a blog to collaborate on a class project. Learning has no temporal or geographic borders, available 24/7 from wherever students and teachers find an internet connection.
This vast landscape of resources is available digitally, freely, and equitably, but before children begin the cerebral trek through the online world, they must learn to do it safely, securely, and responsibly. This conversation used to focus on limiting access to the internet, blocking websites, and layering rules upon rules hoping (vainly) that students would be discouraged from using this infinite and fascinating resource.
It didn’t work.
Best practices now suggest that instead of protecting students, we teach them to be good digital citizens, confident and competent in the use of the internet.
What’s included in K-8 Digital Citizenship Curriculum?
This 70-page text is your guide to what our children must know at what age to thrive in the community called the internet. It’s a roadmap for blending all the pieces into a cohesive, effective student-directed cyber-learning experience that accomplishes ISTE’s general goals to:
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More