Most elementary-age students struggle with typing. This doesn’t surprise me. They’ve been handwriting since kindergarten. They’re proud of their new cursive skills. It’s easy to grab and pencil and write. Typing, though requires setting up their posture, hand position, trying to remember where all those pesky keys are (why aren’t they just alphabetized? It’s a good point. Discuss that with students).
In third grade, I gather the students and we chat about it. Why do they have to learn to keyboard? It’s more than a skill they trot out for the keyboarding software and then forget. Discuss the idea of sharing ideas–the Gutenberg Press, when writing began with scrolls and rocks, why was it important to save ideas in perpetuity? Why is it important to students?
The discussion should come around to the idea that putting ideas in some sort of permanent fashion is important to the history of mankind. The question is how, and the ‘how’ that’s relevant to the students is a comparison of handwriting and keyboarding. Here’s where we go from there: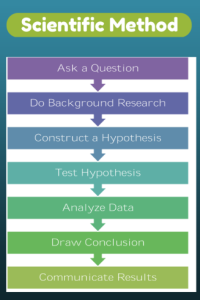
- Discuss whether students handwrite faster/slower than they type. Ask students to share thoughts on why their opinion is true. You are likely to get opinions on both sides of this discussion. If not, prod students with logic for both.
- When it’s clear the class is divided on this subject (or not–that’s fine too), suggest running an experiment to see which is faster—handwriting or typing.
- Circle back to science class and engage in a discussion on the Scientific Method. Develop a hypothesis for this class research, something like: Third grade students in Mr. X’s class can handwrite faster than they type (this is the most common opinion in my classes).
- Have students hand-copy the typing quiz they took earlier in the trimester for 3 minutes.
- Analyze the results: Compare their handwriting speed to their typing speed. I encourage an individual comparison as well as a class average comparison to help with understanding the conclusion.
- Discuss results: Why do students think some students typed faster and others typed slower? (In my classes, third graders typed approx. 10 wpm and handwrote approx. 15 wpm. Discussion was heated and enthusiastic on reasons. Especially valuable were the thoughts of those rare students who typed faster).
- Students will offer lots of reasons for slower typing (they’re new to typing, don’t do it much in class, their hands got off on the keyboard). In truth, the logistics of typing make it the hands-down winner once key placement is secured. Fingers on a keyboard are significantly faster than the moving pencil.
- One reason students suggest is that they don’t usually type from copy. Key in on this reason (quite valid, I think—don’t you?) and revise the experiment to have students type and handwrite from a prompt.
- What is the final conclusion?
- If possible, share results from 4-8th. What grade level do students consistently type faster than they handwrite? Why? Are students surprised by the answer?
- Post a list on the wall of students who type faster than they handwrite. This surprises everyone.
I do this experiment in 3rd, 4th and 5th grade. Third, students on average handwrite faster. By 4th, the average is the same–students can type as fast as they handwrite. This surprises them and energizes them to work harder on their keyboarding. By 5th, most students type faster, though many didn’t expect that.
After this experiment, I see more students selecting keyboarding over handwriting, especially if an iPad is available rather than the cumbersome laptop or desktop. I also see them caring more about the skill of keyboarding as they realize it is their future. This has become an important tool in my keyboarding toolkit that is fully as effective as practicing drills.
For more tricks like this, check out The Essential Guide to Keyboarding in 45 Minutes a Week.
For a lesson plan of this post, click Keyboarding and the Scientific Method.
Note: There are lots of examples of the scientific method and they all vary when talking about elementary grades. Talk to your science teacher and adapt this experiment to the one she uses.
Jacqui Murray has been teaching K-18 technology for 30 years. She is the editor/author of over a hundred tech ed resources including a K-12 technology curriculum, K-8 keyboard curriculum, K-8 Digital Citizenship curriculum. She is an adjunct professor in tech ed, Master Teacher, webmaster for four blogs, an Amazon Vine Voice, CSTA presentation reviewer, freelance journalist on tech ed topics, contributor to NEA Today, and author of the tech thrillers, To Hunt a Sub and Twenty-four Days. You can find her resources at Structured Learning.















































































































2 thoughts on “When is Typing Faster Than Handwriting?”
Comments are closed.