Tag: pedagogy
What is the VARK model of Student Learning?
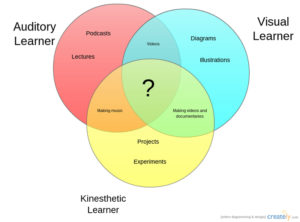 If you use the VARK model of Student Learning, you know why I’m excited about it. VARK started as a questionnaire to help students and teachers understand their best approach to learning but has since become more of a guideline for teaching and learning. The questionnaire is deliberately short (thirteen-sixteen questions, depending upon which version you take) in order to prevent student survey fatigue.
If you use the VARK model of Student Learning, you know why I’m excited about it. VARK started as a questionnaire to help students and teachers understand their best approach to learning but has since become more of a guideline for teaching and learning. The questionnaire is deliberately short (thirteen-sixteen questions, depending upon which version you take) in order to prevent student survey fatigue.
The acronym VARK refers to four learning modalities — Visual, Auditory, Reading/Writing, and Kinesthetic. Though often classroom lessons focus on the Visual, with a bit of preparation, they can be taught using all four modalities thus accommodating students who learn best in a different way. Why go through this extra effort? VARK’s creator, Neil Fleming, explains it this way:
- Students’ preferred learning modes have a significant influence on their behavior and learning.
- Information that is accessed through students’ use of their modality preferences shows an increase in their levels of comprehension, motivation, and metacognition.
For me, that extra time and effort is a no-brainer. Let me back up a moment and explain how I got to that point. I realized after a few years of teaching that something was wrong with the methodology I had been taught. Lots of clever, smart kids weren’t getting what I was putting out. I taught in a way that addressed how the majority learned (because that covered most kids, didn’t it?) but that turned out to be more like a plurality. Or less. In fact, where that plurality of kids might be the biggest group in the class, those that weren’t learning in this prescriptive manner was an even bigger group. To say it another way:
What the Bell Curve considers the “typical student” was always far outnumbered by those who weren’t.
Interestingly enough, Dr. Fleming reports that Kinesthetics (the K in VARK) is the most common learning style though not the most common teaching style.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
What is a Growth Mindset?
 It’s no secret many parents are frustrated with public schools. Are kids learning to think or just to pass tests? Are they spending classroom time wisely or just doing what’s always been done? Are we developing lifelong learners or simply kids who can’t wait to graduate?
It’s no secret many parents are frustrated with public schools. Are kids learning to think or just to pass tests? Are they spending classroom time wisely or just doing what’s always been done? Are we developing lifelong learners or simply kids who can’t wait to graduate?
If this describes you, you’re not alone in your concerns, but there’s hope. Consider a pedagogy that transcends rote memorization and the stock drills often found in today’s classrooms, expects critical thinking that teaches how to learn anything — not just school subjects. It’s called a “Growth Mindset”. In an Edsurge article by Rupa Gupta, former Redesign Administrator at Burnett Middle School in San Jose, Calif., she summarized the issue like this:
“In a recent national survey, 97 percent of teachers agreed that all students can and should have a growth mindset, and that same number said fostering a growth mindset is an important part of a teacher’s job. Yet only 50 percent said they have adequate solutions and strategies to shift mindset.”
So nearly everyone agrees this type of cerebral approach is important to real learning but few know how to make it happen.
What is Growth Mindset?
Let me back up a moment and define “Growth Mindset” more clearly. Most people believe basic human qualities like intelligence and talent are fixed traits: nature supersedes nurture. Kids are born with the characteristics that will mold their future. They are good at math or they aren’t. They can throw a football well or not. As kids grow, they figure out what they can and can’t do and adjust learning and life as needed to these truths. They come to believe that understanding and adapting to this process equates to success.
In a Growth Mindset, people believe ability can be developed through dedication and hard work. The cerebral and physical traits they were born with are just the starting point. Students are responsible for setting the patterns and strategies that allow them to succeed, by evaluating what they can do at any given point and making a plan for learning everything else.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
What is Standards-based Grading?
 How many times have you experienced teachers who based report card grades on how well students complete classwork, homework, and quizzes? They mistakenly conflate these exemplars with learning. For example, a book report may require a certain number of written (or typed) pages or paragraphs rather than evidence that the student drew conclusions and summarized knowledge.
How many times have you experienced teachers who based report card grades on how well students complete classwork, homework, and quizzes? They mistakenly conflate these exemplars with learning. For example, a book report may require a certain number of written (or typed) pages or paragraphs rather than evidence that the student drew conclusions and summarized knowledge.
That’s changing. Today, many educators want to not only evaluate progress at a point in time but optimize that against the ongoing standards their school mission is built on such as Common Core, International Baccalaureate, NGSE, or TEKS.
What is Standards-based Grading
To accomplish this, many schools and Districts have turned to Standards-based Grading. According to Tomlinson and McTighe, standards-based grading (SBG) “measures student proficiency on well-defined course objectives.” This means students have clear guidelines for how to define success over time, making it easy for all stakeholders in a student’s learning to determine if they are accomplishing what must be done for college and career. It de-emphasizes subjectivity by providing an objective delineation of requirements.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
What is #Unschooling?
 The first time I read about Unschooling, I ignored it. Surely, it was a fad that would go away.
The first time I read about Unschooling, I ignored it. Surely, it was a fad that would go away.
When that didn’t happen and I read about it a thousand more times, I dug into it. Inspired by the teachings of John Holt (1923–1985), this free range branch of homeschooling promotes learning through nonstructured, child-led exploration. There’s no set curriculum or schedule; students learn what interests them with guidance from involved adults. There are no worksheets, tests, or structure to provide evidence of learning or templates for teaching. The children pick what to learn, when, at what pace. The result — according to unschoolers, is a love of learning, tenacity to a task, and independent thought that prepares them for college and career better than traditional methods. In fact, if you look at the list of traits valued in popular education programs such as Habits of Mind and Depth of Knowledge, the reasons why parents unschool their children mirror the traits included in these lists.
What is it
According to Dr. Peter Gray of Freedom to Learn:
“Unschooling parents do not … do at home the kinds of things that are done at school. More specifically, they do not establish a curriculum for their children, do not require their children to do particular assignments for the purpose of education, and do not test their children to measure progress. Instead, they allow their children freedom to pursue their own interests and to learn, in their own ways, what they need to know to follow those interests. They may, in various ways, provide an environmental context and environmental support for the child’s learning. In general, unschoolers see life and learning as one.”
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
Visible Learning and John Hattie
 Over the years, I’ve struggled to teach in ways my students would understand. Standing at the front of the classroom stopped working so I researched (and tried in some cases) Whole Brain Teaching (WBT), Socratic Method, Understanding by Design, Mindfulness, and a lot more options that colleagues mentioned as helpful with their differentiated student groups. They all worked for a while and then, maybe when the novelty wore off, I was back to the same Bell curve of successes, failures, and those in between.
Over the years, I’ve struggled to teach in ways my students would understand. Standing at the front of the classroom stopped working so I researched (and tried in some cases) Whole Brain Teaching (WBT), Socratic Method, Understanding by Design, Mindfulness, and a lot more options that colleagues mentioned as helpful with their differentiated student groups. They all worked for a while and then, maybe when the novelty wore off, I was back to the same Bell curve of successes, failures, and those in between.
The same could be said of Standards and curricula adopted in my varied teaching gigs. That includes everything from Common Core to the IB philosophy, from Depth of Knowledge to Project-based Learning. I confess, I found it frustrating. Everything worked for a while and nothing worked in the long term.
That’s when I heard about John Hattie at an education conference I attended and his concept of Visible Learning. John Hattie is a teacher but more significantly, he’s an education researcher. His life’s goal is to determine what education strategies work best for the largest number of students. He engaged in a fifteen-year evaluation of over 50,000 research articles and something like 240 million students — making it the biggest evidence-based education research project ever — and discovered something no one expected and few believed: Almost any approach will work if delivered well. The one foundational element required for success is passionate, involved, committed, flexible teachers:
“The remarkable feature of the evidence is that the greatest effects on student learning occur when teachers become learners of their own teaching, and when students become their own teachers.”
How can that be? According to John Hattie, what he came to call “visible learning” happens when we teachers look at what we’re doing:
“Visible teaching and learning occur when there is deliberate practice aimed at attaining mastery of the goal, when there is feedback given and sought, and when there are active, passionate, and engaging people (teacher, students, peers) participating in the act of learning.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
Is Whole Brain Teaching Right for Me?
 If you have challenging students in your classes, there’s a good chance someone has suggested that you look into Whole Brain Teaching (WBT). Whole Brain Teaching is an active teaching method designed to maximize student engagement in lessons, positive interactions with classmates, and educational fun. Instruction includes vocal directions mixed with hand gestures, inflections, full body movement, head motions, and chants. Studies show that this multi-sensory approach is how the brain is intended to learn and will result in a much greater probability of reaching teaching goals.
If you have challenging students in your classes, there’s a good chance someone has suggested that you look into Whole Brain Teaching (WBT). Whole Brain Teaching is an active teaching method designed to maximize student engagement in lessons, positive interactions with classmates, and educational fun. Instruction includes vocal directions mixed with hand gestures, inflections, full body movement, head motions, and chants. Studies show that this multi-sensory approach is how the brain is intended to learn and will result in a much greater probability of reaching teaching goals.
Where it might have originally been intended for challenging classes — much like Orton-Gillingham started as a multi-sensory learning system for dyslexics — WBT has matured into a strategy that works for lots of learners, even the quiet ones. It uses “model and repeat” as ways to join the right and left sides of the brain (such as the hippocampus, the prefrontal cortex, and the motor cortex) in student learning with the idea that if the entire brain is engaged in learning, there is nothing left over for misbehavior or distraction. For many K-12 teachers, WBT has become their primary teaching strategy.
WBT is based on four core components (called Core Four — part of a longer list of techniques):
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
Sown To Grow: Easily Blend Goal-setting and Reflection into Classwork
 Many of the existential guides for teaching (such as Habits of Mind, the Socrative Method, and Mindfulness) promote a student-driven growth mindset as fundamental to successful learning. This means students take an active part in achieving education and personal goals. The problem is how to persuade students to voluntarily reflect on their progress, rethink goals, and make the required adjustments to achieve success? There’s also the problem of assessing this sort of non-metric thinking. Students and teachers are accustomed to checklists and grading scales. Few have the background to include subjective traits.
Many of the existential guides for teaching (such as Habits of Mind, the Socrative Method, and Mindfulness) promote a student-driven growth mindset as fundamental to successful learning. This means students take an active part in achieving education and personal goals. The problem is how to persuade students to voluntarily reflect on their progress, rethink goals, and make the required adjustments to achieve success? There’s also the problem of assessing this sort of non-metric thinking. Students and teachers are accustomed to checklists and grading scales. Few have the background to include subjective traits.
I found a solution: Sown To Grow. It is an online student-driven performance tracker that uses the metrics of goal-setting and reflection to assess progress. The expectation is that students learn how to learn by assessing their own educational experiences as a way to determine their best strategies to become lifelong learners. Students set their goals, track their progress, and ultimately see what worked and what didn’t. Because this is entirely student-driven, students care more about their work and doing their best. For example, if notetaking worked well as a method of achieving goals in one instance, they can transfer that successful experience to other academic endeavors.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
Is Orton-Gillingham Right For Your Students?
Orton-Gillingham started over seventy years ago as an instructional approach intended for those with difficulty reading, spelling, and writing, like what children experience in dyslexia. Sometimes, teachers recognized the special needs of a reading-challenged student, but just as often, it was blamed on disinterest or lack of effort, leaving the child to conclude s/he “just wasn’t good at reading.” When those same children were taught to read using the Orton-Gillingham (O-G) approach, many felt like that child who puts glasses on for the first time and his/her entire world comes into focus.
Since then, the Orton-Gillingham Method has enabled thousands of children to access worlds opened to them by reading, something they never thought would happen. In fact, it has been so successful, O-G is being mainstreamed into the general education classroom, as a way to unlock the power of reading for more students.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
Is the Socratic Method Right for Your Class?
 Have you ever walked into a classroom where students were engaged in serious on-topic discussion, debating ideas and challenging each other to provide evidence of their statements? And when you looked around for the teacher, s/he was calmly sitting in the back, observing, taking it all in but not participating?
Have you ever walked into a classroom where students were engaged in serious on-topic discussion, debating ideas and challenging each other to provide evidence of their statements? And when you looked around for the teacher, s/he was calmly sitting in the back, observing, taking it all in but not participating?
Chances are, you entered a classroom using a discussion method known as Socratic Debate, aka Socratic Method, Socratic Circle, or Socratic Inquiry. Many teachers try this approach when they realize lecturing doesn’t engage students anymore. Sure, class members can memorize facts but too often the critical thinking required to analyze cause and effect — say, how a specific river encouraged ancient trade — eludes them unless the teacher spells it out, telling them the “right” answer.
In a traditional classroom, asking and answering questions is stressful to many students who are afraid their answer will be wrong. This is where the student-directed, no-right-wrong-answer Socratic Method shines.
What is it
It all started with this (supposed) quote from the iconic Greek thinker, Socrates:
“Let us examine the question together, my friend, and if you can contradict anything I say, do so and I will be persuaded.”
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
How the Frayer Model Helps Thousands Learn Vocabulary
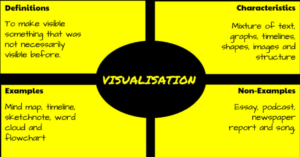 In a perfect world, vocabulary is learned in context: The phrases and sentences around the unknown word define the meaning. If that isn’t sufficient, students use affixes — prefixes, suffixes, and roots — to decode meaning. But because the world isn’t always that pristine, Dorothy Frayer and her colleagues at the University of West Virginia came up with a vocabulary teaching tool that has come to be known as “the Frayer Model”. Now used by thousands of educators, this approach to word study relies on analyzing words rather than memorizing definitions. Somewhat like Concept Circles, the Frayer Model uses a graphical organizer that asks students to describe words by much more than a memorized definition. They must:
In a perfect world, vocabulary is learned in context: The phrases and sentences around the unknown word define the meaning. If that isn’t sufficient, students use affixes — prefixes, suffixes, and roots — to decode meaning. But because the world isn’t always that pristine, Dorothy Frayer and her colleagues at the University of West Virginia came up with a vocabulary teaching tool that has come to be known as “the Frayer Model”. Now used by thousands of educators, this approach to word study relies on analyzing words rather than memorizing definitions. Somewhat like Concept Circles, the Frayer Model uses a graphical organizer that asks students to describe words by much more than a memorized definition. They must:
- define the term
- describe essential characteristics
- provide examples
- provide non-examples
Because the Frayer Model digs deeply into understanding the word, it promotes critical thinking and a granular familiarity with unfamiliar vocabulary. It draws on a student’s prior knowledge to build connections among new concepts and creates a visual reference by which students learn to compare attributes and examples.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More









































