Author: Jacqui
Make your LMS a social learning platform
Vivek Singh, education professional and contributor to Ask a Tech Teacher, has some interesting ideas on using your native LMS as a social learning platform. He has some great thoughts on breakout rooms, discussion forums, virtual reality, and gamifying lessons. I know you’ll enjoy their thoughts:
 Earliest forms of learning, dating back to the stone-age, involved storyboarding one’s experiences on rocks. These photo-stories would prove as a valuable resource for generations to come. Education, thus, has its roots in the earliest social interactions. One of the fundamental qualities that ensured our survival is collaboration through knowledge sharing, imitation and behavior modeling.
Earliest forms of learning, dating back to the stone-age, involved storyboarding one’s experiences on rocks. These photo-stories would prove as a valuable resource for generations to come. Education, thus, has its roots in the earliest social interactions. One of the fundamental qualities that ensured our survival is collaboration through knowledge sharing, imitation and behavior modeling.
Little has changed in today’s space-age. We inadvertently learn from our daily social interactions, with most of our informal learning happens through online sources of information. For example, YouTube, social media, news websites, even self-help videos/blogs which are present in every possible genre. This way of learning is attributed to the advent of the internet which has impacted the adoption of online learning software to facilitate formal education. LMSs are now being accepted as one of the ways to learn smartly. Taking note of the importance of social learning, some LMSs have begun to add features to promote social learning, for those students who are studying online. Learning Management System features that support social interactions amongst students, enhance the learning outcomes for any given online module or course.
What makes your LMS a social learning platform?
Features and activities that enable collaboration among learners could be implemented in the form of chat-boxes, discussion forums, live interactive sessions supporting real-time data sharing capabilities, and many more. Here are some critical features that can essentially leverage an LMS to become social in the true sense.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
Subscriber Special: August
August 2nd only:
Coaching or Mentoring
BOGO — Buy one month; get the second free
Do any of these sound like you?
- Your kindergartners don’t know what ‘enter’, ‘spacebar’, ‘click’ or many other techie words mean but you need to teach them to keyboard, internet, and become digital citizens. How do you start?
- You have new students in your class who haven’t had technology training. The rest of the class has. How do you catch them up?
- Your principal wants you to teach the technology class but you’ve never done it before. What do you do on the first day?
- You’ve been teaching for twenty years but now your Principal wants technology integrated into your class. Where do you start?
- You have a wide mix of tech skills among students in your class. How do you differentiate between student geeks and students who wonder what the right mouse button is for?
- You’ve been tasked with organizing a Technology Use Plan for your school. Where do you start?
- You and colleagues are expected to create a Curriculum Map. How does technology fit into that?
- You love being an edtech professional but what’s your career path?
More and more teachers–both new and experienced–are looking for coaching or mentoring to fill gaps in their learning, keep up to date on the latest teaching strategies, and solve problems they didn’t expect. Many turn to the personalized approach we offer in a collaboration between Ask a Tech Teacher, Jacqui Murray, and Structured Learning. Coaching is completed via Google Hangout with email available for quick questions. After only a short time, teachers find they are better prepared with tech-infused lesson plans, able to teach to standards more fluently, can integrate tech into core classroom time, easily differentiate for student needs with tech, and more.
“Once a month, pick my brain. I’ll share what I’ve learned and what works from 25 years of teaching.” –Jacqui Murray
Normally, we charge a $150 per month with a two month minimum (for a total of $300). This month on the 2nd, get both months of coaching or mentoring for only $150.
Click our PayPal Me here. Add $150.00 to the line.
Because it’s PayPal, you can enter as a guest with any credit card–no PayPal account required.
We wrote the books. We’ll help you deliver on keyboarding, integrating tech into your curriculum, digital citizenship, Common Core, and more. Questions? Ask Jacqui Murray at askatechteacher at gmail dot com.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
August Preview at Ask a Tech Teacher
Here’s a preview of what’s coming up on Ask a Tech Teacher in August:
- Wikispaces has closed. Now what?
- 11 Back-to-school Activities for the First Month of School
- Teaching Digital Rights and Responsibilities
- Websites to teach Moune Skills
- Plan a memorable Back-to-School Night
- The Importance of a Morning Meeting
- Today’s Meet has closed. Alternatives?
- College-level learning online
- How to Teach Critical Thinking
- Tech-ed Resources for your Class
- New Ways to Gamify Learning
- Great Ways to Make Your Class Paper-free
- Differentiating with Personalized Learning
- Back-to-school Activities for teh First Month of School
- Features to make your LMS a social learning platform
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
Last Chance: Building Digital Citizens and Personalized Learning–Grad-level Classes
MTI 557: Building Digital Citizens
This college-credit class starts in one week–Monday, August 6th! Last chance to sign up. Click this link; scroll down to MTI 557 and click for more information and to sign up.
[gallery type="slideshow" ids="59255,59257,59261,59256,59258,59259,59260,59263"]Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
Kiddom Helps Administrators Manage Change
 Kiddom is an easy-to-use learning management system alternative that provides educators with an effective alternative to Google Classroom. Its pages are visual and easy-to-understand, enabling teachers to quickly create lesson plans, find targeted resources, and determine how students are doing. Click here for my full review.
Kiddom is an easy-to-use learning management system alternative that provides educators with an effective alternative to Google Classroom. Its pages are visual and easy-to-understand, enabling teachers to quickly create lesson plans, find targeted resources, and determine how students are doing. Click here for my full review.
What Kiddom does that few other education webtools do is provide free educator and administrator guides on topics such as Standards-based Grading, Blended Learning, and lesson planning (click for my reviews of these). Their newest is the twenty-eight-page ISTE-aligned Change Management eBook. It addresses how to create a sense of urgency, build a coalition, form and communicate your strategic vision, enable action by removing barriers and instituting change, generate short-term wins, and more.
Eric Sheniger, a Senior Fellow at the International Center for Leadership in Education, argues that when considering changes, especially in the realm of education technology, administrators should begin by naming the reasons behind our decision before doing anything else. Start by considering: What is your vision for how technology will be utilized to improve students’ learning outcomes?
In the oft-daunting world of tech-infused education, this guide provides effective strategies to lead the way from wherever you are, be it paper-and-pencil or tech comfort, to where you need to be.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
Technology Turnaround Stories from Hawaii and California
All around the country, schools are turning around education through the use of technology. Here are two, one in Hawaii and one in California that show you steps that might work for you:
[caption id="attachment_59609" align="alignright" width="300"]
 Kalakaua Middle School leadership team gets into the spirit to boost positive behavior.[/caption]
Kalakaua Middle School leadership team gets into the spirit to boost positive behavior.[/caption]
King David Kalakaua MS, Hawaii
When innovative school leaders decided to try a new technology program at King David Kalakaua Middle School this year, they hoped recognizing students’ good behavior would lessen their bad behavior. Their goal was to improve school climate and build positive relationships with everyone on campus by focusing on the positive. In less than six months, not only have they met that goal, but they also changed their peer’s perception of “trouble” students and helped boost grades.
“We feel like it’s had a major impact on students,” says MTSS Coordinator, Tiana Kamiko. She spearheaded the program with her fellow Behavioral Health Specialist Kristen Shimabukuro. “The campus itself feels happier. The kids are smiling more. Just the other day, we had a student telling Kristen that we’re part of the reason he likes to come to school now.”
The idea of rewarding students for positive behavior has a long history in schools, and numerous studies have shown the practice can improve student behavior, reduce suspensions, and even boost student achievement. It is, however, unusual for a school to see such a large jump in so many categories so quickly.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
I’m traveling!
 My Army son is coming to visit from Okinawa Japan for a month. We are training it across country (I’m in California) to visit my Navy daughter in the Washington DC area. Along the way, we’re stopping in Marion Indiana to visit my sister Tina who I haven’t seen in over a decade (though we talk often). I will get to meet many of her extended family I have never met. What a trip!
My Army son is coming to visit from Okinawa Japan for a month. We are training it across country (I’m in California) to visit my Navy daughter in the Washington DC area. Along the way, we’re stopping in Marion Indiana to visit my sister Tina who I haven’t seen in over a decade (though we talk often). I will get to meet many of her extended family I have never met. What a trip!
I am planning to be back to blogging the last week or so of July. Really, it’s hard to keep my fingers off the keys for longer than that. As a result, I won’t be around much. I apologize in advance for missing many of your posts. I will try to drop in now and then but I’m not sure of time constraints.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
Happy Fourth of July!
It’s America’s birthday and I’m celebrating. I have an Army son heading off overseas and a Navy daughter doing her thing stateside. I’m toasting both of them today and all of America’s warriors, God be with you.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
Should you Teach Typing? And Does it Work?
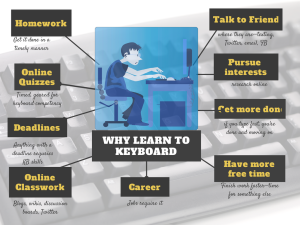 This topic that is close to my tech teacher soul. It has become a familiar argument between those who believe children intuitively learn to type (“see them on smartphones and iPads–they don’t need help”) and those of us who believe instruction makes them better, faster. Ask a Tech Teacher contributor, James Lovelock, discusses this:
This topic that is close to my tech teacher soul. It has become a familiar argument between those who believe children intuitively learn to type (“see them on smartphones and iPads–they don’t need help”) and those of us who believe instruction makes them better, faster. Ask a Tech Teacher contributor, James Lovelock, discusses this:
Explicit typing, simulated application and practical application – Why is this not a thing?
When it comes to education, there has always been a call for approaches that are more grounded in context. For example, you could just look at a map and do some measurements, or you can get out there with a trusty surveyor’s wheel and chart a space and learn real applications. It makes perfect sense to do this, practical application proves relevance and also allows for greater engagement.
Having said that, one would not do this without first explaining the concepts and practicing the basics of measurement. Yet all too often, when it comes to touch-typing that is exactly what occurs, students are expected to just ‘pick it up’ as they go along because the work required to develop the skill correctly can be viewed as “unnecessary,” “too time-consuming,” or “artificial learning.”
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
169 Tech Tip #28: My Sound Doesn’t Work
 In these 169 tech-centric situations, you get an overview of pedagogy—the tech topics most important to your teaching—as well as practical strategies to address most classroom tech situations, how to scaffold these to learning, and where they provide the subtext to daily tech-infused education.
In these 169 tech-centric situations, you get an overview of pedagogy—the tech topics most important to your teaching—as well as practical strategies to address most classroom tech situations, how to scaffold these to learning, and where they provide the subtext to daily tech-infused education.
Today’s tip: #28: My Sound Doesn’t Work
Category: Hardware
Q: I can’t get any sound out of my computer. Do I need a new sound card?
A: Before you invest that kind of money, try these easy fixes:
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More