Author: Jacqui
Ways to use a movie for language teaching
Today, we have a guest post from Philip Perry, founder of Learnclick.com, an online quiz tool lots of teachers use to create and share quizzes. It is also ideal for teaching language as it has many options for asking questions in context. Here, Philip addresses the use of movies in teaching:
 Movies are a great way for learning a language as it helps getting used to the real-life usage. If you are teaching English or any other language you should consider occasionally having your class watch a movie. In this article, we will explore some ways to get the most out of it.
Movies are a great way for learning a language as it helps getting used to the real-life usage. If you are teaching English or any other language you should consider occasionally having your class watch a movie. In this article, we will explore some ways to get the most out of it.
Before you watch a movie together, take some time to introduce it to the class. Start by watching the opening scene and then stop the movie and discuss who the main characters are and summarize the plot.
The following ideas are things you can either do while watching the movie or after having watched the whole movie.
Dialogue: Asking questions about movies is an excellent way to get your students talking. Even the shy ones will be more likely to open up. For example, stop the movie and ask them to predict what will happen next.
moviesheets.com has a database with worksheets for a lot of movies. It can help you with coming up with questions. For example, if you are watching “Oliver Twist” together, you could ask “How were the conditions in the orphanage?”. Or have a more general discussion about what beliefs Dickens was trying to challenge with this story.
Observation: Ask the students to look out for specific items or listen for specific vocabulary words. The first student who sees/hears it, stands up and mentions what he found. As a reward, he gets a candy. Or if you prefer, you can give them a worksheet where they have short phrases and they need to check who said what while they are watching.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
Helping My Daughters Prepare for the ACT Exams
A few months ago, Jane Sandwood sent me a nice note. She’s a a freelance writer, editor and former tutor, homeschooler, and mother of two teenage daughters. She’d read my articles about preparing for SAT/ACTs and had a story of her own detailing how she helped her children prepare for their ACT. I think you’ll enjoy her experiences! 
As spring approaches, my eldest daughter Katherine, now in her junior year, is bracing herself for the upcoming ACT exams, while my youngest, Elizabeth, a sophomore, is getting ready for next year. I am a former tutor and for almost 10 years, I helped students prepare for both SATs and ACTs, relying heavily on tech tools and games to keep them motivated. Somehow, even students who needed the most help weren’t quite as challenging as my own daughters, and the lines between tutor and mom were often blurred, as is to be expected.
Different Learning Styles
Katherine and Elizabeth are just about as different as two people can be when it comes to their attitudes about school and their interests. Katherine, who wishes to be an actor, always took to her studies almost instinctively, since she was a child. She took great pride in handing in her homework neatly, took great pains to finish all her tasks, and was more of a rote learner than Elizabeth, who is more into writing, and who always took a more critical, analytical approach to her studies.
Elizabeth is naturally bright and quick, and has an enviable memory. She has always loved reading and has amassed quite a collection on her Kindle, yet is reticent to complete homework and has always had a strong aversion to maths. Because things tend to come easier to her, she is easily bored and far less disciplined than Kathy when it comes to homework and creating a study strategy. She also struggles with time management, often getting lost in a book or musical album and arriving to school without having completed home tasks.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
How to Prepare for the SAT
 Taking the Scholastic Aptitude Test (SAT) has become a right-of-passage for high school students as they leave formal education and enter the next phase of learning. Over seven million will take SAT tests in 2018 in January, March/April, May, June, October, November, or December. Some will take it for the first time; some for the umpteenth time. For many, it represents a last desperate attempt to qualify for the college of their dreams.
Taking the Scholastic Aptitude Test (SAT) has become a right-of-passage for high school students as they leave formal education and enter the next phase of learning. Over seven million will take SAT tests in 2018 in January, March/April, May, June, October, November, or December. Some will take it for the first time; some for the umpteenth time. For many, it represents a last desperate attempt to qualify for the college of their dreams.
In an earlier article, I focused on preparation for the essay portion of the SAT. This time, I’ll discuss some of the great online sites that help students prepare for the math and reading portions. I’ve based my selections on the following criteria:
- ease of use — accounts are easy to set up with access to both the site and materials quick and intuitive
- well-rounded — nicely differentiated tools that address varied student learning styles
- quantity and quality of available prep materials — materials are both in-depth and in a variety of formats (written, online, video, live/chat) with explanations of answers
- cost vs. value — free is nice but if students get good value for fee-based resources, that’s just as important
- time commitment — students can spend as much or little time as they have on any given day
Here are eleven options for SAT preparation, from my Top Five choices to six Honorable Mentions. All are easy to use, differentiated, up-to-date on the recent changes to the SAT, and represent a good investment of both time and money:
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
17 St. Patrick’s Day Sites For the Classroom
 Getting ready for St. Patrick’s Day? Try these fun websites (check here for updated links):
Getting ready for St. Patrick’s Day? Try these fun websites (check here for updated links):
- Color the shamrock)
- Color the Pot-o-gold
- Color the leprechaun
- Puzzle–St. Pat’s Puzzle
- Puzzle–St. Pat’s puzzle II
- Puzzle–St. Pat’s drag-and-drop puzzle
- Puzzle–St. Pat’s slide puzzle
- Puzzles and games
- St. Patrick’s Day history–video
- St. Pat’s Day songs–video
- Tic tac toe
- Webquest for St. Patrick’s Day I
- Webquest II
- Wordsearch
If you have iPads at your school, try these three apps:
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
International Blog Delurking Week–Get Involved!
 Believe it or not, there is an International Blog Delurking Week that traditionally takes place in the first full week of January. It’s an opportunity for bloggers to find out who quietly reads their blog without commenting. As Melissa the founder of this event says:
Believe it or not, there is an International Blog Delurking Week that traditionally takes place in the first full week of January. It’s an opportunity for bloggers to find out who quietly reads their blog without commenting. As Melissa the founder of this event says:
“…there is a huge discrepancy between the number of readers in actuality and the number of readers I actually know are reading. Or a tongue-twister like that.”
Yep, I noticed I missed that week. I was still getting the year started! But Melissa also says you can run it anytime you want so I’m taking advantage of that codicil.
OK, another yep–comments are always closed on this blog. So here’s what I’d love you to do:
- Follow Ask a Tech Teacher (sign up in the sidebar)
- Sign up for my newsletter
- Like and Follow us on Facebook
- Follow us on Twitter
If you do, you’ll probably find one of us over at your social media, checking things out in your corner of the tech ed world. We love a good road trip!
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
169 Tech Tip #26: My Mouse Doesn’t Work
 In these 169 tech-centric situations, you get an overview of pedagogy—the tech topics most important to your teaching—as well as practical strategies to address most classroom tech situations, how to scaffold these to learning, and where they provide the subtext to daily tech-infused education.
In these 169 tech-centric situations, you get an overview of pedagogy—the tech topics most important to your teaching—as well as practical strategies to address most classroom tech situations, how to scaffold these to learning, and where they provide the subtext to daily tech-infused education.
Today’s tip: #26: My Mouse Doesn’t Work
Category: Hardware
Q: My mouse stopped working. Do I need a new one?
A: Maybe, but try a few things first:
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
39 Resources for Read Across America Day
Many people in the United States, particularly students, parents and teachers, join forces on Read Across America Day, annually held on March 2. This nationwide observance coincides with the birthday of Dr. Seuss.
 Here are some great reading websites for students K-5:
Here are some great reading websites for students K-5:
- Aesop Fables—no ads
- Aesop’s Fables
- Audio stories
- Childhood Stories
- Classic Fairy Tales
- Fairy Tales and Fables
- Listen/read–Free non-fic audio books
- Starfall
- Stories read by actors
- Stories to read for youngsters
- Stories to read–II
- Stories—MeeGenius—read/to me
- Stories—non-text
- Story Scramble
- Ziggity Zoom Stories (more…)
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
169 Tech Tip #25: My Desktop Keyboard Doesn’t Work
 In these 169 tech-centric situations, you get an overview of pedagogy—the tech topics most important to your teaching—as well as practical strategies to address most classroom tech situations, how to scaffold these to learning, and where they provide the subtext to daily tech-infused education.
In these 169 tech-centric situations, you get an overview of pedagogy—the tech topics most important to your teaching—as well as practical strategies to address most classroom tech situations, how to scaffold these to learning, and where they provide the subtext to daily tech-infused education.
Today’s tip: #25: My Desktop Keyboard Doesn’t Work
Category: Hardware
Q: I need to type a lesson plan, but all I get is a cursor that blinks… and blinks… but goes nowhere. What do I do?
A: The first culprit to investigate is the keyboard. Try these solutions:
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
What is the VARK model of Student Learning?
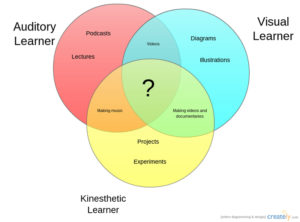 If you use the VARK model of Student Learning, you know why I’m excited about it. VARK started as a questionnaire to help students and teachers understand their best approach to learning but has since become more of a guideline for teaching and learning. The questionnaire is deliberately short (thirteen-sixteen questions, depending upon which version you take) in order to prevent student survey fatigue.
If you use the VARK model of Student Learning, you know why I’m excited about it. VARK started as a questionnaire to help students and teachers understand their best approach to learning but has since become more of a guideline for teaching and learning. The questionnaire is deliberately short (thirteen-sixteen questions, depending upon which version you take) in order to prevent student survey fatigue.
The acronym VARK refers to four learning modalities — Visual, Auditory, Reading/Writing, and Kinesthetic. Though often classroom lessons focus on the Visual, with a bit of preparation, they can be taught using all four modalities thus accommodating students who learn best in a different way. Why go through this extra effort? VARK’s creator, Neil Fleming, explains it this way:
- Students’ preferred learning modes have a significant influence on their behavior and learning.
- Information that is accessed through students’ use of their modality preferences shows an increase in their levels of comprehension, motivation, and metacognition.
For me, that extra time and effort is a no-brainer. Let me back up a moment and explain how I got to that point. I realized after a few years of teaching that something was wrong with the methodology I had been taught. Lots of clever, smart kids weren’t getting what I was putting out. I taught in a way that addressed how the majority learned (because that covered most kids, didn’t it?) but that turned out to be more like a plurality. Or less. In fact, where that plurality of kids might be the biggest group in the class, those that weren’t learning in this prescriptive manner was an even bigger group. To say it another way:
What the Bell Curve considers the “typical student” was always far outnumbered by those who weren’t.
Interestingly enough, Dr. Fleming reports that Kinesthetics (the K in VARK) is the most common learning style though not the most common teaching style.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More
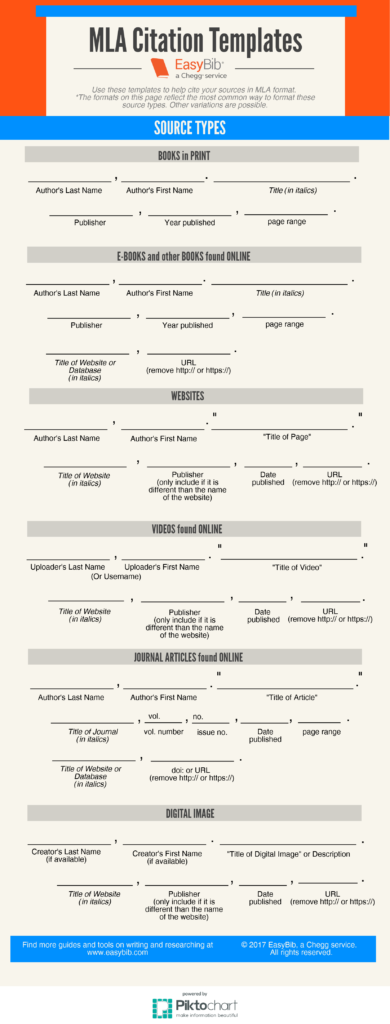
Citing Sources: The Infographic
EasyBib, the first name most educators think of when citing sources, has created a useful summary on MLA guidelines for citing sources. Best of all, it’s an infographic you can grab and post on your wall (with proper citation, of course):
Click here for the original post.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- More